Abstract
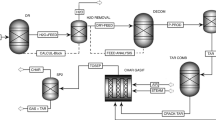
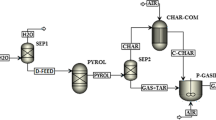
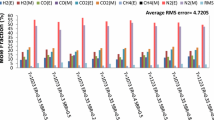
Thermochemical gasification is a potential energy extraction pathway that converts biomass to gaseous fuel and chemical feedstock. Modelling of biomass gasification is an efficient and economical method to predict the gaseous fuel characteristics compared to experimentation, which incurs additional time and effort. The present work deals with kinetic modelling and analysis of CaO enabled biomass gasification to analyse the effect of steam to biomass ratio, sorbent addition and residence time on syngas composition in MATLAB platform. The model is developed by applying Arrhenius reaction kinetics for homogeneous, heterogeneous and tar cracking reactions associated with gasification. Rate of gasification, tar cracking and carbonation reactions are incorporated in the model to predict the effect of residence time of solid and gaseous reaction species in the final syngas constitution. Rate of generation of each chemical species is determined by considering the cumulative effect of reaction kinetics of the reactions considered. The developed model is validated for product gas composition with the experimental results of air–steam gasification. An RMS error of 3.66 is reflected when the model estimated syngas composition for air–steam gasification is compared with that of the experimental results. The uniqueness of the model is that it can predict the temporal variation of syngas species for steam-assisted air gasification in sorbent enabled environment for CO2 capture. It is also found that at a temperature of 1000 K, equivalence ratio of 0.25 and steam to biomass ratio of unity, H2 mole fraction has no appreciable increase beyond a sorbent to biomass ratio of 1. The developed model can be used to predict the effect of residence time on syngas composition for air–steam biomass gasification (with and without sorbent) for a steam to biomass ratio and sorbent to biomass ratio range of 0–2.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelouahed, L., Authier, O., Mauviel, G., Corriou, J. P., Verdier, G., & Dufour, A. (2012). Detailed modeling of biomass gasification in dual fluidized bed reactors under aspen plus. Energy and Fuels, 26(6), 3840–3855. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef300411k
Baruah, D., & Baruah, D. C. (2014). Modeling of biomass gasification: a review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.129
Basu, P. (2010). Biomass gasification and pyrolysis. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2009-0-20099-7
Blasi, C. D. (2000). Dynamic behaviour of stratified downdraft gasifiers. Chemical Engineering Science, 55(15), 2931–2944. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00562-X
Campoy, M., Gómez-Barea, A., Villanueva, A. L., & Ollero, P. (2008). Air-steam gasification of biomass in a fluidized bed under simulated autothermal and adiabatic conditions. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 47(16), 5957–5965. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie800220t
Deepanraj, B., Lawrence, P., Sivashankar, R., & Sivasubramanian, V. (2016). Analysis of pre-heated crude palm oil, palm oil methyl ester and its blends as fuel in a diesel engine. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 37(5), 495–500. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2015.1004106
Deepanraj, B., Sivasubramanian, V., & Jayaraj, S. (2015). Experimental and kinetic study on anaerobic digestion of food waste: the effect of total solids and pH. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 7(6), 063104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4935559
Di Blasi, C. (2004). Modeling wood gasification in a countercurrent fixed-bed reactor. AIChE Journal, 50(9), 2306–2319. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.10189
Florin, N. H., & Harris, A. T. (2008). Enhanced hydrogen production from biomass with in situ carbon dioxide capture using calcium oxide sorbents. Chemical Engineering Science, 63(2), 287–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2007.09.011
Global Energy Review. (2021). IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2021
Gómez-Barea, A., & Leckner, B. (2010). Modeling of biomass gasification in fluidized bed. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 36(4), 444–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2009.12.002
Gomez-Barea, A., Nilsson, S., Barrero, F. V., & Campoy, M. (2010). Devolatilization of wood and wastes in fluidized bed. Fuel Processing Technology, 91(11), 1624–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.06.011
Inayat, A., Ahmad, M. M., Mutalib, M. I. A., & Yusup, S. (2012). Process modeling for parametric study on oil palm empty fruit bunch steam gasification for hydrogen production. Fuel Processing Technology, 93(1), 26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.08.014
Jess, A. (1996). Mechanisms and kinetics of thermal reactions of aromatic hydrocarbons from pyrolysis of solid fuels. Fuel, 75(12), 1441–1448. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(96)00136-6
Ji, P., Feng, W., & Chen, B. (2009). Production of ultrapure hydrogen from biomass gasification with air. Chemical Engineering Science, 64(3), 582–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2008.10.015
Khunchit, K., Nitayavardhana, S., & Ramaraj, R. (2020). Liquid hot water extraction as a chemical-free pretreatment approach for biobutanol production from Cassia fi stula pods. Fuel, 279(May), 118393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118393
Kumar, A., Kumar, N., Baredar, P., & Shukla, A. (2015). A review on biomass energy resources, potential, conversion and policy in India. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 45, 530–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.007
Loha, C., Chattopadhyay, H., & Chatterjee, P. K. (2013). Energy generation from fluidized bed gasification of rice husk. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4816496
Nikoo, M. B., & Mahinpey, N. (2008). Simulation of biomass gasification in fluidized bed reactor using ASPEN PLUS. Biomass and Bioenergy, 32(12), 1245–1254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2008.02.020
Pauls, J. H., Mahinpey, N., & Mostafavi, E. (2016). Simulation of air-steam gasification of woody biomass in a bubbling fluidized bed using Aspen Plus: A comprehensive model including pyrolysis, hydrodynamics and tar production. Biomass and Bioenergy, 95, 157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.10.002
Puig-Arnavat, M., Bruno, J. C., & Coronas, A. (2010). Review and analysis of biomass gasification models. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2010.07.030
Radmanesh, R., Chaouki, J., & Guy, C. (2012). Biomass gasification in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor: experiments and modeling. AIChE Journal, 52(12), 4258–4272. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic
Rupesh, S., Muraleedharan, C., & Arun, P. (2015). A comparative study on gaseous fuel generation capability of biomass materials by thermo-chemical gasification using stoichiometric quasi-steady-state model. International Journal of Energy and Environmental Engineering, 6(4), 375–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-015-0182-0
Rupesh, S., Muraleedharan, C., & Arun, P. (2016). ASPEN plus modelling of air–steam gasification of biomass with sorbent enabled CO2 capture. Resource-Efficient Technologies, 2(2), 94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2016.07.002
Safarian, S., Unnþórsson, R., & Richter, C. (2019). A review of biomass gasification modelling. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 110(May), 378–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.003
Saxena, R. C., Seal, D., Kumar, S., & Goyal, H. B. (2008). Thermo-chemical routes for hydrogen rich gas from biomass: a review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2007.03.005
Senthilkumar, N., Deepanraj, B., Vasantharaj, K., & Sivasubramanian, V. (2016). Optimization and performance analysis of process parameters during anaerobic digestion of food waste using hybrid GRA-PCA technique. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4972884
Singh, D., Sharma, D., Soni, S. L., Sharma, S., Kumar Sharma, P., & Jhalani, A. (2020). A review on feedstocks, production processes, and yield for different generations of biodiesel. Fuel, 262(October), 116553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116553
Sreejith, C. C., Muraleedharan, C., & Arun, P. (2015). Air-steam gasification of biomass in fluidized bed with CO2 absorption: A kinetic model for performance prediction. Fuel Processing Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.09.040
Sues, A., Juraščík, M., & Ptasinski, K. (2010). Exergetic evaluation of 5 biowastes-to-biofuels routes via gasification. Energy, 35(2), 996–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.06.027
Tuomi, S., Kaisalo, N., Simell, P., & Kurkela, E. (2015). Effect of pressure on tar decomposition activity of different bed materials in biomass gasification conditions. Fuel, 158, 293–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.05.051
Westbrook, C. K., & Dryer, F. L. (1984). Chemical kinetic modeling of hydrocarbon combustion. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 10(1), 1–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-1285(84)90118-7
Xu, G., Murakami, T., Suda, T., Kusama, S., & Fujimori, T. (2005). Distinctive effects of CaO additive on atmospheric gasification of biomass at different temperatures. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 44(15), 5864–5868. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie050432o
Yang, W., Ponzio, A., Lucas, C., & Blasiak, W. (2006). Performance analysis of a fixed-bed biomass gasifier using high-temperature air. Fuel Processing Technology, 87(3), 235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2005.08.004
Yu, L., Lu, J., Zhang, X., & Zhang, S. (2007). Numerical simulation of the bubbling fluidized bed coal gasification by the kinetic theory of granular flow (KTGF). Fuel, 86(5–6), 722–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.09.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
S, R., C, M. & P, A. Influence of Residence Time on Syngas Composition in CaO Enhanced Air–Steam Gasification of Biomass. Environ Dev Sustain 24, 8363–8377 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01787-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01787-1