Abstract
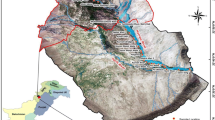
Toxic metals and metalloids (TMMs) in soil can be accumulated in crops, which poses potential risks to human health. In this paper, 55 topsoil and 23 crop samples, collected in Qilihe, China, were selected to study the contamination, risk, and plant accumulation of TMMs in soil-crop system. TMM concentrations in soil samples were all below the permissible limits, but Hg and Cd exhibited the potential ecological risk due to their slight accumulation in soil. There was slight Hg pollution in 2 samples of Lanzhou lily (Lilium davidii), and 1 sample of radish (Raphanus sativus), Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis), and welsh onions (Allium fistulosum) due to Hg’s strong bio-accumulation, but there was no risk to human health. The TMM accumulation in leaf crops was large, followed in tuber and seed crops. Available potassium, cation exchange capacity, soil organic matter, and available phosphate were the main factors associated with TMM accumulation in crops among the selected soil properties. This study shows the current contamination situation and the predominant influencing factors associated with the accumulation of TMMs in 24 crops, which provides the emphasis and direction of relative policies in land use and crop plantation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bravo S, Amoros JA, Perez DLRC, Garcia FJ, Moreno MM, Ormeno SM, Hibueras P (2015) Influence of the soil pH in the uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Pb and Mn) and other elements (Ca, K, Al, Sr and Ba) in vine leaves, Castilla-La Mancha (Spain). J Geochem Explor 174:79–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.12.012
Chandra R, Bharagava RN, Yadav S, Mohan D (2009) Accumulation and distribution of toxic metals in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Indian mustard (Brassica campestris L.) irrigated with distillery and tannery effluents. J Hazard Mater 162(2-3):1514–1521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.040
Chen SB, Zhu YG, Yang JC (2003) Mechanism of the effect of phosphorus on bioavailability of heavy metals in soil-plant systems. Tech Equip Environ Pollut Control 4(8):1–7. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-9108.2003.08.001
Chen HM, Zhu YG, Dong YH (2005) Environmental soil science. Science Press, Beijing, China
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512-513:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (1990) Background values of soil elements in China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67(1):489–512. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-112301
Duan K, Zhao B, Zhang S, Ma Y (2020) Contamination characteristics, source analysis, and ecological risk assessment of toxic metals and metalloid in agricultural soil in Yuzhong, China. J Environ Qual 50:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jeq2.20163
Emurotu JE, Onianwa PC (2017) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in soil and selected food crops cultivated in Kogi State, north central Nigeria. Environ Syst Res 6(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-017-0098-1
Fayiga AO, Nwoke OC (2017) Metal (Loid)s in farmland soils and strategies to reduce bioavailability. J Environ Biol 2(1):9–24. https://doi.org/10.17352/ojeb.000003
Förstner U, Ahlf W, Calmano W, Kersten M (1990) Sediment criteria development. In: Heling D, Rothe P, Förstner U, Stoffers P (eds) Sediments and Environmental Geochemistry. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-75097-7_18
Gao H, Bai J, Wang Q, Huang L, Xiao R (2010) Profile distribution of soil nutrients in unrestored and restored wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China. Procedia Environ Sci 2:1652–1661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.176
Guo W, Dai JL, Wang RQ (2012) Progress in the effect of dissolved organic matter on adsorption of heavy metals by soil. Chin J Soil Sci 43(03):761–768. https://doi.org/10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2012.03.043
Gupta DK, Chatterjee S, Datta S, Veer V, Walther C (2014) Role of phosphate fertilizers in heavy metal uptake and detoxification of toxic metals. Chemosphere 108:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.01.030
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
He LL, Wang M, Zhang GL, Qiu GN, Cai DQ, Wu ZY, Zhang X (2015) Remediation of Cr(VI) contaminated soil using long-duration sodiumthiosulfate supported by micro–nano networks. J Hazard Mater 294:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.052
Horiguchi H, Oguma E, Sasaki S, Miyamoto K, Kayama F (2004) Dietary exposure to cadmium at close to the current provisional tolerable weekly intake does not affect renal function among female Japanese farmers. Environ Res 95(1):20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-9351(03)00142-7
Hu B, Jia X, Hu J, Xu D, Xia F, Li Y (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil-plant-human system in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(9):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14091042
Jiao W, Chen W, Chang AC, Page AL (2012) Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long-term phosphate fertilizers applications: a review. Environ Pollut 168:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.03.052
Kelepertzis E (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma 221:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.01.007
Khalil H, Schwartz C, El Hamiani O, Kubiniok J, Morel JL, Boularbah A (2013) Distribution of major elements and trace metals as indicators of technosolisation of urban and suburban soils. J Soils Sediments 13(3):519–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-012-0594-x
Khan A, Khan S, Khan MA, Qamar Z, Waqas M (2015) The uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by food plants, their effects on plants nutrients, and associated health risk: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(18):13772–13799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4881-0
Li Q, Chen Y, Fu H, Cui Z, Shi L, Wang L, Liu Z (2012) Health risk of heavy metals in food crops grown on reclaimed tidal flat soil in the Pearl River Estuary, China. J Hazard Mater 227-228:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.023
Li JB, Su Z, Zhou ZC, Ji RL, Zhang M (2016) Analysis on characteristics of soil salinity in Shazaoyuan site of Gansu Beishan region. J Arid Land Res Environ 30(09):115–120. https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2016.292
Li X, Shen H, Zhao Y, Cao W, Hu C, Sun C (2019) Distribution and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in water, sediments, and aquatic macrophytes: a case study of the junction of four rivers in Linyi City, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(16):2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162861
Liao Z, Chen Y, Ma J, Islam MS, Weng L, Li Y (2019) Cd, Cu, and Zn accumulations caused by long-term fertilization in greenhouse soils and their potential risk assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(15):2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152805
Liu Y, Xiao T, Perkins RB, Zhu J, Zhu Z, Xiong Y, Ning Z (2016) Geogenic cadmium pollution and potential health risks, with emphasis on black shale. J Geochem Explor 176:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.04.004
Mayuri C, Amit M, Arvind KN, Sanjay KG, Rajendra KK (2016) Heavy metal contamination in vegetables grown around peri-urban and urban-industrial clusters in ghaziabad, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 22(3):736–752. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2015.1105723
Minase NA, Masafu MM, Geda AE, Wolde AT (2016) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of Central Ethiopia: the contribution of land use types and organic sources to their variability. Open J Soil Sci 6:99–112 https://doi.org/10.4236/ojss.2016.66011
National Health and Family Planning Commission of PRC (2017) National standard for food safety - limit of contaminants in food, GB 2762-2012. China Standards Press, Beijing
Nie JH, Liu XM, Wang QR (2004) Effects of nutrient elements on the lead uptake by hyperaccumulators. Ecol Environ Sci (03):306–309. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2004.03.002
Park JH, Bolan N, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2011) Comparative value of phosphate sources on the immobilization of lead, and leaching of lead and phosphorus in lead contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 409(4):853–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.11.003
Peng J, Li F, Zhang J, Chen Y, Cao T, Tong Z, Zhao X (2019) Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals pollution of farmland soil and crops in Jilin Province. Environ Geochem Health 42:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00416-1
Pierangeli MAP, Guilherme LRG, Oliveira LR, Curi N, Silva MLN (2001) Effect of ionic strength of the equilibrium solution upon lead adsorption/desorption in Brazilian Oxisols. Pesq Agrop Brasileira 36(8):1077–1084. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2001000800010
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E (2011) Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 213:113–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_4
Rai PK, Lee SS, Zhang M, Tsang YF, Kim KH (2019) Heavy metals in food crops: health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ Int 125:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.067
Remon E, Bouchardon JL, Cornier B, Guy B, Leclerc JC, Faure O (2005) Soil characteristics, heavy metal availability and vegetation recovery at a former metallurgical landfill: Implications in risk assessment and site restoration. Environ Pollut 137(2):316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.01.012
Seshadri B, Bolan NS, Choppala G, Kunhikrishnan A, Sanderson P, Wang H, Currie LD, Tsang DCW, Ok YS, Kim G (2017) Potential value of phosphate compounds in enhancing immobilization and reducing bioavailability of mixed heavy metal contaminants in shooting range soil. Chemosphere 184:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.172
Silveira MLA, Alleoni LRF, Guilherme LRG (2003) Biosolids and heavy metals in soils. Sci Agric 60 (4):793–806. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162003000400029
Tong J, Guo H, Wei C (2014) Arsenic contamination of the soil–wheat system irrigated with high arsenic groundwater in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Sci Total Environ 496:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.073
Tu, C., Zheng, C. R., & Chen, H M. (2000). Effect of applying chemical fertilizers on forms of lead and cadmium in red soil. Chemosphere, 41(1-2), 0–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00400-2, 133
USEPA (2011) United States Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System. Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS). U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC http://www.epa.gov/iris/
Wang B, Xue S, Liu GB, Zhang GH, Li G, Ren ZP (2012) Changes in soil nutrient and enzyme activities under different vegetations in the Loess Plateau area, Northwest China. Catena 92:196–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.12.004
Wang F, Huang C, Chen Z, Bao K (2019) Distribution, ecological risk assessment, and bioavailability of cadmium in soil from Nansha, Pearl River Delta, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(19):3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193637
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int Sch Res Not 2011:1–20. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/402647
Xiao JJ, Ma HX, Lu CT (2013) Study on spatial distribution of soil nutrients and comprehensive evaluation of nutrients in low mountain-hilly region of Sichuan Province, China. Appl Mech Mater 295-298:2544–2548. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.295-298.2544
Xu D, Chen Z, Sun K, Yan D, Kang M, Zhao Y (2013) Effect of cadmium on the physiological parameters and the subcellular cadmium localization in the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 97:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.07.021
Yang J, Guo H, Ma Y, Wang L, Wei D, Hua L (2010) Genotypic variations in the accumulation of Cd exhibited by different vegetables. J Environ Sci 22(8):1246–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60245-X
Yang X, Chen X, Yang X (2019) Effect of organic matter on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in a black soil from Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res 187:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2018.11.016
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21467013, 21167007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: BZ, SZ, KD; data curation: SZ, YM; formal analysis: KD; funding acquisition: BZ; investigation: KD, XP, PY; methodology: KD; project administration: SZ, YM; resources: SZ, YM; software: KD; supervision: SZ; validation: XP, PY; visualization: KD, BZ; writing – original draft: KD; writing – review and editing: BZ, SZ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors have agreed for authorship, read and approved the manuscript
Consent for publication
All authors have given consent for publishing this study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, K., Zhang, S., Zhao, B. et al. Soil contamination and plant accumulation characteristics of toxic metals and metalloid in farmland soil–food crop system in Qilihe, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 50063–50073 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14175-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14175-z