Abstract
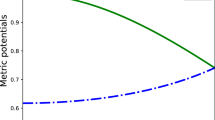
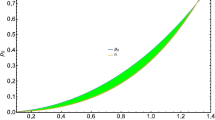
We obtain new regular exact solutions to the field equations for uncharged relativistic stellar objects with vanishing pressure anisotropy. We assume a quadratic equation of state and a choice of measure of anisotropy and a metric function defining one of the gravitational potentials. In our exact models, we regain anisotropic and isotropic results generated by other researchers as a special case. It is interesting that our results are in agreement with Minkowski space–time and earlier Einstein models. The physical analysis of the plots reveals that the gravitational potentials and matter variables are well behaved in the stellar interior. Using our model, we generate finite relativistic stellar masses which are consistent with the astronomical objects previously found by other researchers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K Schwarzschild, Sitz. Deut. Akad. Wiss. Math. Phys. 24, 424 (1916)
M Ishak, Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics (Geneva, 2015)
M K Mak and T Harko, Eur. Phys. J. C 73, 2585 (2013)
R Leijon, The Einstein field equations on semi-Riemannian manifolds and the Schwarzschild solution (Umea Universitet, Sweden, 2012)
R L Bowers and E P T Liang, Astrophys. J. 188, 657 (1974)
K Dev and M Gleiser, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 13, 1389 (2004)
R Ruderman, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 10, 427 (1972)
S Karmakar, S Mukherjee, R Sharma and S D Maharaj, Pramana – J. Phys. 68, 881 (2007)
N Pant, N Pradhan and M H Murad, Astrophys. Space Sci. 355, 2156 (2014)
M K Mak and T Harko, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 459, 393 (2003)
H Panahi, R Monadi and I Eghdami, Chin. Phys. Lett. 33(7), 072601 (2016)
L Herrera and W Barreto, Astrophysics 1, 2824 (2013)
M K Mak and T Harko, Chin. J. Astrophys. 2, 248 (2002)
N Pant, N Pradhan and M Malaver, Int. J. Astrophys. Sci. 3, 1 (2015)
K Dev and M Gleiser, Gen. Rel. Grav. 35, 1435 (2003)
M Kalam, F Rahaman, M Hossein and S Ray, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 3319 (2013)
J M Sunzu, S D Maharaj and S Ray, Astrophys. Space Sci. 354, 517 (2014)
M Malaver, Wirel. Sensor Netw. 36, 2392 (2016)
M H Murad and S Fatema, Astrophys. Space Sci. 350, 293 (2014)
P Mafa Takisa and S D Maharaj, Astrophys. Space Sci. 361, 262 (2016)
S D Maharaj and P Mafa Takisa, Gen. Rel. Grav. 44, 1419 (2012)
M Malaver, J. Mod. Phys. 1(1), 6 (2014)
D K Matondo and S D Maharaj, Astrophys. Space Sci. 361, 221 (2016)
S Thirukkanesh and F S Ragel, Pramana – J. Phys. 78(5), 687 (2012)
M Spaans and J Silk, Astrophys. J. 538, 115 (2000)
B Kinasiewicz and P Mach, Acta Phys. Pol. B 38, 39 (2007)
T Harko and M K Mak, Astrophys. Space Sci. 361, 1 (2016)
J M Sunzu, Global J. Sci. Front. Res. 18, 1 (2018)
S Thirukkanesh and F C Ragel, Astrophys. Space Sci. 352, 743 (2014)
M Malaver, Am. J. Astron. Astrophys. 1, 41 (2013)
J M Sunzu and K A Mahali, Global J. Sci. Front. Res. 18, 19 (2018)
P Bhar, M Govender and R Sharma, Pramana – J. Phys. 90: 5 (2018)
A Das, A Bannerjee, S Chakraborty and S Pan, Pramana – J. Phys. 90, 19 (2018)
J M Sunzu and P Danford, Pramana – J. Phys. 89: 44 (2017)
M Malaver, Wirel. Sensor Netw. 92, 327 (2018)
M Esculpi and E Aloma, Eur. Phys. J. C 67, 521 (2010)
R Sharma and S D Maharaj, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 375, 1265 (2007)
T Harko and K S Cheng, Phys. Lett. A 266, 249 (2000)
H Sotani, K Kohri and T Harada, Phys. Rev. D 69, 084008 (2004)
P Mafa Takisa and S D Maharaj, Astrophys. Space Sci. 343, 569 (2013)
S Thirukkanesh and S D Maharaj, Class. Quantum Grav. 25, 235001 (2008)
T Feroze and A A Siddiqui, Gen. Rel. Grav. 43, 1025 (2011)
S A Ngubelanga, S D Maharaj and S Ray, Astrophys. Space Sci. 357, 74 (2015)
M Malaver, Front. Math. Appl. 1, 9 (2014)
M C Durgapal and R Bannerji, Phys. Rev. D 27, 328 (1983)
A Krasinski, Inhomogeneous cosmological models (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997)
J M Sunzu, S D Maharaj and S Ray, Astrophys. Space Sci. 352, 719 (2014)
S D Maharaj, J M Sunzu, and S Ray, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 129, 3 (2014)
P H Chavanis and T Harko, Astrophys. Space Sci. 361, 1 (2016)
J M Sunzu, New models for quark stars with charge and anisotropy, Ph.D. thesis (University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 2014)
M K Mak and T Harko, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 13, 149 (2004)
P C C Freire, C G Bassa, N Wex and I H Stairs, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 412, 2763 (2011)
R P Negreiros, F Weber, M Malheiro and V Usov, Phys. Rev. D 80, 083006 (2009)
M Dey, I Bombaci, J Dey, S Ray and B C Samanta, Phys. Lett. B 438, 123 (1998)
T Güver, F Ozel, A Cabrera-Lavers and P Wroblewski, Astrophys. J. 712, 964 (2010)
T Güver, P Wroblewski, L Camarota and F Ozel, Astrophys. J. 719, 1807 (2010)
T Gangopadhyay, S Ray, X D Lix, J Dey and M Dey, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 431(4), 3216 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the University of Dodoma for providing conducive environment, resources and other research facilities. Secondly, Mashiku would like to thank the District Executive Director at Kwimba District in Mwanza region for providing a two-year study leave.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunzu, J.M., Thomas, M. New stellar models generated using a quadratic equation of state. Pramana - J Phys 91, 75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-018-1650-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-018-1650-x
Keywords
- Einstein field equations
- vanishing pressure anisotropy
- uncharged stellar object
- quadratic equation of state