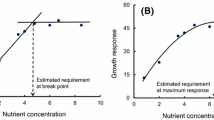
Abstract
The principles of modern aquaculture encourage the development of fish feeds containing low fish meal content and several types of plant ingredients plus nutrients to avoid depleting global fish stocks and to reduce costs. However, food constituents can affect animal nutrition and feeding behavior, so the effect of different diets on fish behavior and growth needs to be understood to optimize the use of nutrients and to improve fish welfare. The development of multiple-choice self-feeding systems led to a new perspective for investigating these issues in aquaculture species. Our purpose with this review is to summarize the information that has been published to date on this topic and to identify gaps in knowledge where research is needed. Key subjects are assessed under the following major headings: How do we study dietary selection in fish? What food signals do fish use to choose the right diet? and How do fish respond to food challenges? The present review will provide a picture of the main results obtained to date in these studies in aquaculture fish species, as well as perspectives for future research in the field.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanärä A, Brännäs E (1996) Dominance in demand-feeding behaviour in Arctic charr and rainbow trout: the effect of stocking density. J Fish Biol 48:242–254
Almaida-Pagán PF, Rubio CV, Mendiola P, De Costa J, Madrid JA (2006) Macronutrient selection through post-ingestive signals in sharpsnout seabream fed gelatine capsules and challenged with protein dilution. Physiol Behav 88:550–558
Almaida-Pagán PF, Seco-Rovira V, Hernández MD, Madrid JA, De Costa J, Mendiola P (2008) Energy intake and macronutrient selection in sharpsnout seabrean (Diplodus puntazzo) challenged with fat dilution and fat deprivation using encapsulated diets. Physiol Behav 93:474–480
Anglade I, Wang Y, Jensen J, Tramu G, Kah O, Conlon JM (1994) Characterization of trout galanin and its distribution in trout brain and pituitary. J Comp Neurol 350:63–74
Aranda A, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Zamora S, Madrid JA (2000) Self-design of fish diets by means of self-feeders: validation of procedures. J Physiol Biochem 56:155–166
Aranda A, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Madrid JA (2001) Effect of short-term fasting on macronutrient self-selection in sea bass. Physiol Behav 73:105–109
Atienza MT, Chatzifotis S, Divanach P (2004) Macronutrient selection by sharp snout seabream (Diplodus puntazzo). Aquaculture 5:481–491
Azzaydi M, Madri JA, Zamora S, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Martínez FJ (1998) Effect of three feeding strategies (automatic, ad libitum demand-feeding and time restricted demand-feeding) on feeding rhythms and growth in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 163:285–296
Baker B, Booth DA, Duggan JP, El Gibson (1987) Protein appetite demonstrated: learned specificity of protein-cue preference to protein need in adult rats. Nutr Res 7:481–486
Baker B, Levy A, Hall L, Lightman S (1995) Cloning and expression of melanin-concentrating hormone genes in the rainbow trout brain. Neuroendocrinology 61:67–76
Bartumeus F, Da Luz MGE, Viswanathan GM, Catalan J (2005) Animal search strategies: a quantitative random-walk analysis. Ecology 86:3078–3087
Bellinger LL, Williams FE, Rogers QR, Gietzen DW (1996) Liver denervation attenuates the hypophagia produced by an imbalanced amino acid diet. Physiol Behav 59:925–929
Berthoud HR, Seeley RJ (2000) Neural control of macronutrient selection. CRC Press, Washington
Blomqvist AG, Soderberg C, Lundell I, Milner RJ, Larhammar D (1992) Strong evolutionary conservation of neuropeptide Y: sequences of chicken, goldfish, and Torpedo marmorata DNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:2350–2354
Bombardelli RA, Syperreck MA, Sanches EA (2006) Hormônio liberador de gonadotrofinas em peixes: aspectos básicos e suas aplicações. Arquivos de Ciências Veterinária e Zoologia 9:59–65 (In Portuguese)
Booth D, Baker BJ (1990) DL-Fenfluramine challenge to nutrient-specific textural preference conditioned by concurrent presentation of two diets. Behav Neurosci 104:226–229
Bosma RH, Verdegem MCJ (2011) Sustainable aquaculture in ponds: principles, practices and limits. Livest Sci 139:58–68
Boujard T, Le Gouvello R (1997) Voluntary feed intake and discrimination of diets containing a novel fluoroquinolone in self-fed rainbow trout. Aquat Living Resour 10:343–350
Brännäs E, Strand Å (2015) A test of “nutritional wisdom” in perch (Perca fluviatilis) by self-selection of encapsulated macronutrients. Appl Anim Behav Sci 171:219–225
Cerdá-Reverter JM, Peter RE (2003) Endogenous melanocortin antagonist in fish: structure, brain mapping, and regulation by fasting of the goldfish agouti-related protein gene. Endocrinology 144:4552–4561
Cerdá-Reverter JM, Martinez-Rodriguez G, Zanuy S, Carrillo M, Larhammar D (2000) Molecular evolution of the neuropeptide Y (NPY) family of peptides: cloning of three NPY-related peptides from the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Regul Pept 95:25–34
Conceição LEC, Aragão C, Richard N, Engrola S, Gavaia P, Mira S, Dias J (2009) Avanços recentes em nutrição de larvas de peixes. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia 38:26–35 (In Portuguese)
Cuenca E, Diz M, De La Higuera G (1993) Self-selection of a diet covering zinc needs in the trout. In: Kaushik S, Luquet J (eds) Fish nutrition in practice. INRA, pp 413–418
FAO (2009) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2008. FAO, Rome
FAO (2011) Fisheries and Aquaculture Department. In: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department [online]. Rome. Updated 22 July 2011. Cited 29 August 2011
Favreau A, Baumont R, Duncan AJ et al (2010) Sheep use preingestive cues as indicators of postingestive consequences to improve food learning. J Anim Sci 88:1535–1544
Forbes JM (2001) Consequences of feeding for future feeding. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 128:463–470
Fortes-Silva R, Martínez FJ, Villaroel M, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2010) Daily feeding patterns and self-selection of dietary oil in Nile tilapia. Aquac Res 42:157–160
Fortes-Silva R, Martínez FJ, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2011a) Macronutrient selection in Nile tilapia fed gelatin capsules and challenged with protein dilution/restriction. Physiol Behav 102:356–360
Fortes-Silva R, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Martínez FJ (2011b) Effects of pretreating a plant-based diet with phytase on diet selection and nutrient utilization in European sea bass. Aquaculture 319:417–422
Fortes-Silva R, Rosa PV, Zamora S, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2012) Dietary self-selection of protein-unbalanced diets supplemented with three essential amino acids in Nile tilapia. Physiol Behav 105:639–644
Freeland WJ, Janzen DH (1974) Strategies in herbivory by mammals: the role of plant secondary compounds. Am Nat 108:269–289
Geurden I, Cuvier A, Gondouin E, Olsen RE, Ruohonen K, Kaushik S, Boujard T (2005) Rainbow trout can discriminate between feeds with different oil sources. Physiol Behav 85:107–114
Geurden I, Corraze G, Boujard T (2007) Self-feeding behaviour of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, offered diets with distinct feed oils. Appl Anim Behav Sci 108:313–326
Heberlein M, Turner DC (2009) Dogs, Canis familiaris, find hidden food by observing and interacting with a conspecific. Anim Behav 78:385–391
Hidalgo F, Kentouri M, Divanach P (1988) Sur l’utilisation du self feeder comme outil d’epreuve nutritionnelle du loup, Dicentrarchus labrax résultats préliminaires avec la méthionine. Aquaculture 68:177–190 (In French)
Holt DE, Johnston CE (2011) Can you hear the dinner bell? response of cyprinid fishes to environmental acoustic cues. Anim Behav 82:529–534
Illius AW, Gordon IJ (1993) Diet selection in mammalian herbivores: constraints and tactics. In: Hughes RN (ed) Diet selection: an interdisciplinary approach to foraging behaviour. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 157–180
Kaslin J, Nystedt JM, Ostergard M, Peitsaro N, Panula P (2004) The orexin/hypocretin system in zebrafish is connected to the aminergic and cholinergic systems. J Neurosci 24:2678–2689
Katz D (1937) Animals and man. Studies in comparative psychology. Longmans, Green & Co., London
Kulczykowska E, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2010) Neurohormonal regulation of feed intake and response to nutrients in fish: aspects of feeding rhythm and stress. Aquac Res 41:654–667
López M, Lelliott CJ, Vidal-Puig A (2007) Hypothalamic fatty acid metabolism: a housekeeping pathway that regulates food intake. Bio Essays 29:248–261
Madrid JA, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Martínez FJ (2009) La nutrición y alimentación en acuicultura “Alimentación en piscicultura” Fundación Observatorio Español de Acuicultura, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y Medio Rural y Marino, p 698 (In Spanish)
Martinez JB, Chatzifotis S, Divanach P, Takeuchi T (2004) Effect of dietary taurine supplementation on growth performance and feed selection of sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax fry fed with demand-feeders. Fish Sci 70:74–79
Montoya A, Alves Martins D, Yúfera M, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2011) Self-selection of diets with different oil oxidation levels in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 314:282–284
Newman JA, Parsons AJ, Harvey A (1992) Not all sheep prefer clover: diet selection revisited. J Agric Sci 119:275–283
Owen KQ, Knabe DAK, Burgoon G, Gregg EJ (1994) Self-selection of diets and lysine requirements of growing-finishing swine. J Anim Sci 72:554–564
Paspatis M, Kentouri M, Krystalakis N (1997) Vitamin C: a factor on feed preference of sea bream (Sparus aurata). In: Proceedings of the 5th Hellenic symposium on 361 oceanography and fisheries, Kavala, Greece, pp 169–172
Pereira-Da-Silva EM, Orsoli DN, Araújo LF, Cantelmo OA, Merighe JKF (2004) Regulação da ingestão protéica na tilápia do Nilo, Oreochromis niloticus. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia 33:1921–1927 (In Portuguese)
Peters JC, Harper AE (1984) Influence of dietary protein level on protein self selection and plasma and brain amino acid concentrations. Physiol Behav 33:783–790
Peyon P, Lin XW, Himick BA, Peter RE (1998) Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding brain preprocholecystokinin in goldfish. Peptides 19:199–210
Provenza FD, Villalba JJ, Cheney CD, Werner SJ (1998) Self-organization of foraging behavior: from simplicity to complexity without goals. Nutr Res Rev 11:199–222
Raubenheimer D, Tucker D (1997) Associative learning by locusts: pairing of visual cues with consumption of protein and carbohydrate. Anim Behav 54:1449–1459
Raubenheimer D, Simpson S, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Huntingford F, Kadri S, Jobling M (2012) Nutrition and diet choice. In: Huntingford F, Jobbing M, Kadri S (eds) Aquaculture and behavior. Wiley, New York, pp 150–182
Richter CP (1943) Total self-regulatory functions in animals and human beings. Harvey Lect Ser 38:61–103
Rubio VC, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Madrid JA (2003) Macronutrient selection through postingestive signals in sea bass fed on gelatine capsules. Physiol Behav 78:795–803
Rubio VC, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Madrid JA (2005a) Fish macronutrient selection through post-ingestive signals: effect of selective macronutrient deprivation. Physiol Behav 84:651–657
Rubio VC, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Madrid JA (2005b) Effects of salinity on food intake and macronutrient selection in European sea bass. Physiol Behav 85:333–339
Rubio VC, Sanchez-Vazquez FJ, Madrid JA (2006a) Oral serotonin administration affects the quantity and the quality of macronutrients selection in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax L. Physiol Behav 87:7–15
Rubio VC, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Madrid JA (2006b) Influence of nutrient preload on encapsulated macronutrient selection in European sea bass. Physiol Behav 89:662–669
Rubio VC, Navarro DB, Madrid JA, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2009) Macronutrient self-selection in Solea senegalensis fed macronutrient diets and challenged with dietary protein dilutions. Aquaculture 291:95–100
Ruohonen K, Simpson SJ, Raubenheimer D (2007) A new approach to diet optimisation: a re-analysis using European whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus). Aquaculture 267:147–156
Rymer T, Schradin C, Pillay N (2008) Social transmission of information about novel food in two populations of the African striped mouse, Rhabdomys pumilio. Anim Behav 76:1297–1304
Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Martínez M, Zamora S, Madrid JA (1994) Design and performance of an accurate demand feeder for the study of feeding behaviour in sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. Physiol Behav 56:789–794
Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Madrid JA, Zamora S (1995a) Circadian rhythms of feeding activity in sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L: dual phasing capacity of diel demand feeding pattern. J Biol Rhythm 10:256–266
Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Zamora S, Madrid JA (1995b) Light-dark and food restriction cycles in Sea bass: effect of conflicting zeitgebers on demand feeding rhythms. Physiol Behav 58:705–714
Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Yamamoto T, Akiyama T, Madrid JA, Tabata M (1998) Selection of macronutrients by goldfish operating self-feeders. Physiol Behav 65:211–218
Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Yamamoto T, Akiyama T, Madrid JA, Tabata M (1999) Macronutrient self-selection through demand-feeders in rainbow trout. Physiol Behav 66:45–51
Siegel PB, Gustin SJ, Katanbaf MN (2011) Motor ability and self-selection of an analgesic drug by fast-growing chickens. J Appl Poult Res 20(3):249–252
Simpson SJ, Raubenheimer D (1996) Feeding behaviour, sensory physiology and nutrient feedback: a unifying model. Entomol Exp Appl 80:55–64
Simpson SJ, Raubenheimer D (2001) A framework for the study of macronutrient intake in fish. Aquac Res 32:421–432
Simpson SJ, White PR (1990) Associative learning and locust feeding: evidence for a “learned hunger” for protein. Anim Behav 40:506–513
Soengas JL (2014) Contribution of glucose- and fatty acid sensing systems to the regulation of food intake in fish. A review. Gen Comp Endocrinol 205:36–48
Unniappan S, Lin X, Cervini L, Rivier J, Kaiya H, Kangawa K, Peter RE (2002) Goldfish ghrelin: molecular characterization of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid, partial gene structure and evidence for its stimulatory role in food intake. Endocrinology 143:4143–4146
Viswanathan GM, Buldyrev SV, Havlin S, Da Luz MGE, Raposo EP, Stanley HE (1999) Optimizing the success of random searches. Nature 401:911–914
Vivas M, Rubio VC, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ, Mena C, García García B, Madrid JA (2006) Dietary self-selection in sharpsnout seabream (Diplodus puntazzo) fed paired macronutrient feeds and challenged with protein dilution. Aquaculture 251:430–437
Volko VH, Bjorklund JM, Peter RE (1999) Stimulation of feeding behavior and food consumption in the goldfish, Carassius auratus, by orexin-A and orexin-B. Brain Res 846:204–209
Volpato GL (2007) Considerações metodológicas sobre os testes de preferência na avaliação do bem-estar em peixes. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia 36:53–61 (In Portuguese)
Wang Y, Conlon JM (1994) Purification and characterization of galanin from the phylogenetically ancient fish, the bowfin (Amia calva) and dogfish (Scyliorhinus canicula). Peptides 15:981–986
Xia B, Wang J, Gao Q, Sun Y, Zhang L, Ma J, Liu X (2015) The nutritional contributions of dietary protein sources to tissue growth and metabolism of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka): evidence from nitrogen stable isotope analysis. Aquaculture 435:237–244
Yamamoto T, Shima T, Furuita H, Suzuki N, Sanchez-Vázquez FJ, Tabata M (2001) Self-selection and feed consumption of diets with a complete amino acid composition and a composition deficient in either methionine or lysine by rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquac Res 32:83–91
Yamamoto T, Shima T, Furuita H, Suzuki N (2003) Effect of water temperature and short-term fasting on macronutrient self-selection by common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 220:655–666
Acknowledgments
Developing the report that led to this review was primarily sponsored by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MICINN) by projects (AGL2010-22139-C03-01 and AQUAGENOMICS) to FJSV and (CNPq, Pesquisador Visitante Especial/PVE, 401416/2014-3) to R. Fortes-Silva, although the material has been updated since that report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, R.F., Kitagawa, A. & Sánchez Vázquez, F.J. Dietary self-selection in fish: a new approach to studying fish nutrition and feeding behavior. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 26, 39–51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-015-9410-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-015-9410-1