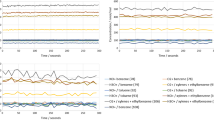
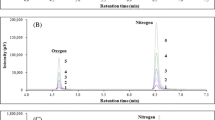
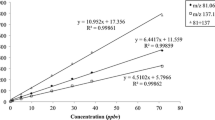
Abstract
Henry’s law constant is an essential parameter for the estimation of the environmental prevalence of pollutants. Here, we present two improved methods for measuring Henry’s law constant deploying inert gas stripping (IGS). The methods are targeted at compounds with high gamma coefficients (activity coefficient at infinite dilution) corresponding to large infinite dilution coefficients, such as monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes. We deploy a highly sensitive PTR-MS (proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometer) (low limit of detection, wide linear range, split-second time resolution) as detector. We use suited off-equilibrium conditions to extrapolate to equilibrium conditions. The first method is based on the observed linear correlation between gas flow and off-equilibrium experimental Henry’s law constant value. The second method is based on the linear dependence of the gas holdup on volumetric flow. We report HLC constants for six monoterpenes, isoprene and even, as a proof of concept, the sesquiterpene farnesene. The new methods allow for measuring HLC of nearly insoluble compounds at a new accuracy and precision.

ᅟ



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PTR-MS:
-
Proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometry
- HLC:
-
Henry’s law constant (moles per atmosphere)
- IGS:
-
Inert gas stripping
- IGS/PTR-MS:
-
Inert gas stripping coupled with PTR-MS
- m/z:
-
Mass to charge ratio
- sccm :
-
Standard cubic centimeters per minute
References
Abraham, M., Ballantine, D., & Callihan, B. (2000). Revised linear solvation energy relationship coefficients for the 77-phase McReynolds data set based on an updated set of solute descriptors. Journal of Chromatography A, 878(1), 115–124. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00143-6.
Abraham, M. H., Sánchez-Moreno, R., Cometto-Muñiz, J. E., & Cain, W. S. (2007). A quantitative structure–activity analysis on the relative sensitivity of the olfactory and the nasal trigeminal chemosensory systems. Chemical Senses, 32(7), 711–719. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjm038.
Aprea, E., Biasioli, F., Mark, T., & Gasperi, F. (2007). PTR-MS study of esters in water and water/ethanol solutions: fragmentation patterns and partition coefficients. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 262(1–2), 114–121. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2006.10.016.
Bobadilla, R., Huybrechts, T., Dewulf, J., & Van Langenhove, H. (2003). Determination of the Henry’s constant of volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds of environmental concern by the BAS (batch air stripping) technique: a new mathematical approach. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 48(3), 7–11.
Caputi, L., & Aprea, E. (2011). Use of terpenoids as natural flavouring compounds in food industry. Recent Patents on Food, Nutrition & Agriculture, 3(1), 9–16.
ChemSpider—The free chemical database http://www.chemspider.com/. (20120 06 02 and 04). http://www.chemspider.com/. Accessed 3 June 2012.
Cho, J. S., & Wakao, N. (1988). Determination of liquid-side and gas-side volumetric mass transfer coefficients in a bubble column. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 21(6), 576–581. doi:10.1252/jcej.21.576.
Copolovici, L. O., & Niinemets, Ü. (2005). Temperature dependencies of Henry’s law constants and octanol/water partition coefficients for key plant volatile monoterpenoids. Chemosphere, 61(10), 1390–1400. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.003.
Dearden, J., & Schuurmann, G. (2003). Quantitative structure–property relationships for predicting Henry’s law constant from molecular structure. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22(8), 1755–1770.
Duhem, P., & Vidal, J. (1978). Extension of the dilutor method to measurement of high activity coefficients at infinite dilution. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2(3), 231–235. doi:10.1016/0378-3812(78)80012-0.
Eckert, C. A., & Sherman, S. R. (1996). Measurement and prediction of limiting activity coefficients. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 116(1–2), 333–342. doi:10.1016/0378-3812(95)02904-4.
EPA/OPPT/Exposure Assessment Tools and Models/Estimation Program Interface (EPI) Suite Version 3.12 (August 17, 2004). http://www.epa.gov/oppt/exposure/pubs/episuite.htm. Accessed 3 June 2012.
Hansel, A., Jordan, A., Holzinger, R., Prazeller, P., Vogel, W., & Lindinger, W. (1995). Proton-transfer reaction mass-spectrometry—online trace gas-analysis at the ppb level. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 149, 609–619. doi:10.1016/0168-1176(95)04294-U.
Hilal, S., Ayyampalayam, S., & Carreira, L. (2008). Air-liquid partition coefficient for a diverse set of organic compounds: Henry’s. Law constant in water and hexadecane. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(24), 9231–9236. doi:10.1021/es8005783.
Hoff, J. T., Mackay, D., Gillham, R., & Shiu, W. Y. (1993). Partitioning of organic chemicals at the air-water interface in environmental systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 27(10), 2174–2180. doi:10.1021/es00047a026.
Kantarci, N., Borak, F., & Ulgen, K. O. (2005). Bubble column reactors. Process Biochemistry, 40(7), 2263–2283. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.10.004.
Karl, T., Prazeller, P., Mayr, D., Jordan, A., Rieder, J., Fall, R., & Lindinger, W. (2001). Human breath isoprene and its relation to blood cholesterol levels: new measurements and modeling. Journal of Applied Physiology, 91(2), 762–770.
Karl, T., Yeretzian, C., Jordan, A., & Lindinger, W. (2003). Dynamic measurements of partition coefficients using proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS). International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 223(1–3), 383–395.
Lei, Y., Shunthirasingham, C., & Wania, F. (2007). Comparison of headspace and gas-stripping techniques for measuring the air-water partititioning of normal alkanols (C4 to C10): effect of temperature, chain length, and adsorption to the water surface. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 52(1), 168–179. doi:10.1021/je060344q.
Leroi, J.-C., Masson, J.-C., Renon, H., Fabries, J.-F., & Sannier, H. (1977). Accurate measurement of activity coefficient at infinite dilution by inert gas stripping and gas chromatography. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 16(1), 139–144. doi:10.1021/i260061a609.
Li, J., Dallas, A. J., Eikens, D. I., Carr, P. W., Bergmann, D. L., Hait, M. J., & Eckert, C. A. (1993). Measurement of large infinite dilution activity coefficients of nonelectrolytes in water by inert gas stripping and gas chromatography. Analytical Chemistry, 65(22), 3212–3218. doi:10.1021/ac00070a008.
Li, J., Shen, C., Wang, H., Han, H., Zheng, P., Xu, G., & Chu, Y. (2008a). Dynamic measurements of Henry’s law constant of aromatic compounds using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 24(4), 705–708.
Li, J.-Q., Shen, C.-Y., Wang, H.-M., Han, H.-Y., Zheng, P.-C., Xu, G.-H., & Chu, Y.-N. (2008b). Dynamic measurements of Henry’s law constant of aromatic compounds using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 24(04), 705–708. doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB20080428.
Lindinger, W., Hansel, A., & Jordan, A. (1998a). Proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS): on-line monitoring of volatile organic compounds at pptv levels. Chemical Society Reviews, 27(5), 347–354. doi:10.1039/A827347Z.
Lindinger, W., Hansel, A., & Jordan, A. (1998b). On-line monitoring of volatile organic compounds at pptv levels by means of proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS)—medical applications, food control and environmental research. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 173(3), 191–241. doi:10.1016/S0168-1176(97)00281-4.
Liu, D., Feilberg, A., Nielsen, A. M., & Adamsen, A. P. S. (2013). PTR-MS measurement of partition coefficients of reduced volatile sulfur compounds in liquids from biotrickling filters. Chemosphere, 90(4), 1396–1403. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.068.
Luebke, W. (2012, April 2). Farnesene 502-61-4 thegoodscentscompany.com. flavor and fragrance article. http://www.thegoodscentscompany.com/data/rw1044061.html. Accessed 3 June 2012.
Mackay, D., Shiu, W. Y., & Sutherland, R. P. (1979). Determination of air-water Henry’s law constants for hydrophobic pollutants. Environmental Science & Technology, 13(3), 333–337. doi:10.1021/es60151a012.
Meylan, W., & Howard, P. (2005). Estimating octanol-air partition coefficients with octanol-water partition coefficients and Henry’s law constants. Chemosphere, 61(5), 640–644. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.029.
ORCHYD - ORganic Compounds HYDration properties database. (2012). http://orchyd.asu.edu/. Accessed 2 June 2012.
Pollien, P., Jordan, A., Lindinger, W., & Yeretzian, C. (2003). Liquid-air partitioning of volatile compounds in coffee: dynamic measurements using proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 228(1), 69–80. doi:10.1016/S1387-3806(03)00197-0.
Richon, D., Sorrentino, F., & Voilley, A. (1985). Infinite dilution activity coefficients by the inert gas stripping method: extension to the study of viscous and foaming mixtures. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 24(4), 1160–1165. doi:10.1021/i200031a044.
Roberts, D., & Acree, T. (1996). Retronasal flavor release in oil and water model systems with an evaluation of volatility predictors. Flavor-Food Interactions, 633, 179–187.
Roth, C., Goss, K., & Schwarzenbach, R. (2002). Adsorption of a diverse set of organic vapors on the bulk water surface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 252(1), 21–30. doi:10.1006/jcis.2002.8446.
Sander, R. (1999a). Compilation of Henry’s law constants for inorganic and organic species of potential importance in environmental chemistry (version 3). http://www.mpch-mainz.mpg.de/~sander/res/henry.html, Accessed 8 July 2009.
Sander, R. (1999b). Modeling atmospheric chemistry: interactions between gas-phase species and liquid cloud/aerosol particles. Surveys in Geophysics, 20(1), 1–31.
Schuhfried, E., Biasioli, F., Aprea, E., Cappellin, L., Soukoulis, C., Ferrigno, A., & Gasperi, F. (2011). PTR-MS measurements and analysis of models for the calculation of Henry’s law constants of monosulfides and disulfides. Chemosphere, 83(3), 311–317. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.051.
Schuhfried, E., Probst, M., Limtrakul, J., Wannakao, S., Aprea, E., Cappellin, L., … Biasioli, F. (2013). Sulfides: chemical ionization induced fragmentation studied with proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometry density functional calculations. Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 48(3), 367–378. doi:10.1002/jms.3153.
Shunthirasingham, C., Lei, Y., & Wania, F. (2007). Evidence of bias in air-water Henry’s law constants for semivolatile organic compounds measured by inert gas stripping. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(11), 3807–3814. doi:10.1021/es062957t.
Sigma-Aldrich. (retrieved 20120603). Farnesene, mixture of isomers | Sigma-Aldrich. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/w383902?lang=de®ion=AT. Accessed 3 June 2012.
Staudinger, J., & Roberts, P. V. (2001). A critical compilation of Henry’s law constant temperature dependence relations for organic compounds in dilute aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 44(4), 561–576. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00505-1.
Trelea, I., Atlan, S., Deleris, I., Saint-Eve, A., Marin, M., & Souchon, I. (2008). Mechanistic mathematical model for in vivo aroma release during eating of semiliquid foods. Chemical Senses, 33(2), 181–192. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjm077.
Weidenhamer, J. D., Macias, F. A., Fischer, N. H., & Williamson, G. B. (1993). Just how insoluble are monoterpenes? Journal of Chemical Ecology, 19(8), 1799–1807. doi:10.1007/BF00982309.
Yeretzian, C., Jordan, A., & Lindinger, W. (2003). Analysing the headspace of coffee by proton-transfer-reaction mass-spectrometry. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 223(1–3), 115–139. doi:10.1016/S1387-3806(02)00785-6.
Acknowledgments
Work partly supported by Provincia Autonoma di Trento—AP 2012 (FB, EA).
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Erna Schuhfried is a former member
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 169 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuhfried, E., Aprea, E., Märk, T.D. et al. Refined Measurements of Henry’s Law Constant of Terpenes with Inert Gas Stripping Coupled with PTR-MS. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 120 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2337-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2337-2