Abstract
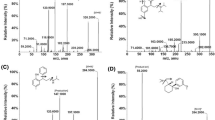
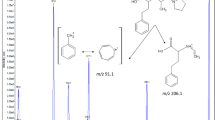
Given that there are many autopsy cases in which erectile dysfunction (ED) treatment drugs can be detected from elderly men who are diagnosed to have died of cardiovascular disorders, the degree of cardiovascular risk posed by ED treatment drugs is still controversial. Moreover, counterfeit ED drugs or illegal dietary supplements containing ED drugs are also threats to public health. In this study, we established a detailed procedure for simultaneous analysis of typical ED drugs (sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil) and their metabolites in human blood and urine by isotope dilution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS). Each sample of whole blood and urine containing the three ED treatment drugs, their metabolites, and deuterated internal standards (ISs) was diluted with alkalinized water, loaded onto an Oasis HLB cartridge, washed with dilute ammonium hydroxide solution, and eluted with chloroform. The eluate was acidified with methanol and concentrated HCl and evaporated to dryness. The resulting residue was reconstituted with methanol and mobile phase solution, and 5 μl of the solution was injected into an LC–MS–MS instrument. The determinations were made by multiple reaction monitoring using each product ion. The recovery rates of the drugs, metabolites, and ISs from whole blood and urine ranged from 80.7 to 127%. Good linearity was obtained for all drugs and their metabolites in the range of 1–100 ng/ml in whole blood and urine with correlation coefficients greater than 0.99. The detection limits (signal-to-noise ratio = 3) for all compounds were not higher than 0.05 ng/ml. Intraday and interday accuracy and precision data were also satisfactory for all compounds in whole blood and urine. Actual measurements of sildenafil and N-desmethyl sildenafil were also demonstrated by analysis of whole blood and urine specimens from two male volunteers after ingestion of a 25-mg tablet of sildenafil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padma-Nathan H (2005) Sildenafil citrate, the classic PDE 5 inhibiter, a five-year review of its efficacy and safety in the arena of erectile dysfunction. In: Gregory AP (ed) Oral pharmacotherapy for male sexual dysfunction. A guide to clinical management. Humana, Totowa, pp 65–83
Yang W, Lee S, Choi Y, Chung H (2009) Importance of sildenafil analysis for drug screening of postmortem specimens: demonstration of five autopsy cases involving sildenafil. Forensic Toxicol 27:107–109
Kudo K, Ishida T, Hikiji W, Usumoto Y, Umehara T, Nagamatsu K, Tsuji A, Ikeda N (2010) Pattern of poisoning in Japan: selection of drugs and poisons for systematic toxicological analysis. Forensic Toxicol 28:25–32
Singh S, Prasad B, Savaliya AA, Shah RP, Gohil VM, Kaur A (2009) Strategies for characterizing sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil and their analogues in herbal dietary supplements, and detecting counterfeit products containing these drugs. Trends Anal Chem 28:13–28
Man CN, Nor NM, Lajis R, Harn GL (2009) Identification of sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry on short capillary column. J Chromatogr A 1216:8426–8430
Strano-Rossi S, Anzillotti L, de la Torre X, Botrè F (2010) A gas chromatography/mass spectrometry method for the determination of sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil and their metabolites in human urine. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24:1697–1706
Dumestre-Toulet V, Cirimele V, Gromb S, Belooussoff T, Lavault D, Ludes B, Kintz P (2002) Last performance with VIAGRA®: postmortem identification of sildenafil and its metabolites in biological specimens including hair sample. Forensic Sci Int 126:71–76
Zhu X, Xiao S, Chen B, Zhang F, Yao S, Wan Z, Yang D, Han H (2005) Simultaneous determination of sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil as forbidden components in natural dietary supplements for male sexual potency by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatgr A 1066:89–95
Pistos C, Papoutsis I, Dona A, Stefanidou M, Athanaselis S, Maravelias C, Spiliopoulou C (2008) Off-line HPLC method combined to LC–MS for the determination of sildenafil and its active metabolite in post-mortem human blood according to confirmation criteria. Forensic Sci Int 178:192–198
Alkharfy KM (2009) Simple and sensitive LC–ESI–MS method for the quantitation of sildenafil in plasma samples. J Sep Sci 32:3866–3870
Lewis RJ, Johnson RD, Blank CL (2006) Quantitative determination of sildenafil (Viagra®) and its metabolite (UK-103, 320) in fluid and tissue specimens obtained from six aviation fatalities. J Anal Toxicol 30:14–20
Ku H-Y, Shon J-H, Liu K-H, Shin J-G, Bae SK (2009) Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of vardenafil and its major metabolite, N-desethylvardenafil, human plasma: application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B 877:95–100
Inoue S, Miyamoto S, Ogasawara M, Endo O, Suzuki G (2009) Simultaneous determination of medicinal ingredients in so-called health-promoting food using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with a pentafluorophenyl stationary phase. J Health Sci 55:183–191
Witjes BC, Ahsman MJ, van der Nagel BC, Tibboel D, Mathot RA (2010) Simultaneous assay of sildenafil and desmethylsildenafil in neonate plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr 24:180–185
Challa BR, Awen BZ, Chandu BR, Khagga M, Bannoth CK, Kanala K, Shaik RP, Peraman R, Gogineni R (2010) Sildenafil and N-desmethyl sildenafil quantification in human plasma by HPLC coupled with ESI–MS/MS detection: application to bioequivalence study. Anal Methods 2:1043–1050
TIAFT (2011) Reference blood level list of therapeutic and toxic substances. http://www.tiaft.org/node/36. Cited Aug 2011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasegawa, K., Suzuki, O., Gonmori, K. et al. Simultaneous analysis of sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, and their desalkyl metabolites in human whole blood and urine by isotope dilution LC–MS–MS. Forensic Toxicol 30, 25–32 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-011-0125-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-011-0125-2