Abstract
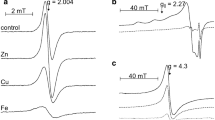
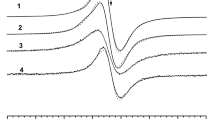
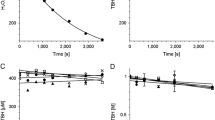
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) studies of complexes of chloroquine with melanin synthesized from 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) confirmed an important role ofo-semiquinone free radicals during the drug binding by melanin. Chloroquine increases free radical concentration in DOPA-melanin. It has been also demonstrated that chloroquine binding to melanin is modified by metal ions. Co2+ ions reduce and Zn2+ ions increase the concentration of free radicals in both DOPA-melanin and melanin-chloroquine complexes. Free radical properties of melanin strongly depend on the presence of oxygen (O2) in the environment of the sample. Interactions of melanin and oxygen molecules cause a decrease of the free radical concentration in the samples and a narrowing of the EPR lines. Higher values of both spin-spin and spin-lattice relaxation times were determined for melanin samples in air than for evacuated samples. Application of the observed effects in oximetry is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buszman E.: Habilitation thesis, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland 1994.
Buszman E., Kopera M., Wilczok T.: Biochem. Pharmacol.33, 7–11 (1984)
Pasenkiewicz-Gierula M., Sealy R.C.: Biochim. Biophys. Acta884, 510–516 (1986)
Sarna T., Hyde J.S., Swartz H.M.: Science192, 1132–2234 (1976)
Sealy R.C., Felix C.C., Hyde J.S., Swartz H.M. in: Free Radicals in Biology (Pryor W.A., ed.), vol. IV, pp. 209–259. New York: Academic Press 1980.
Jastrzębska M.M., Isotalo H., Paloheimo J., Stubb H., Pilawa B.: J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed.7, 781–793 (1996)
Pilawa B., Buszman E., Latocha M., Wilczok T. in: Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Physics and Engineering in Health Care jointly held with 12th Congress of the Polish Society of Medical Physics, p. 49. Poznań 2001.
Binns F., Chapman R.F., Robson N.C., Swan G.A., Waggott A.J.: J. Chem. Soc. C1970, 1128–1134.
Wertz J.E., Bolton J.R.: Electron Spin Resonance: Elementary Theory and Practical Applications. New York: Chapman and Hall 1986.
Sczaniecki B. in: Radiospektroskopia Ciała Stałego (Stankowski J., ed.), pp. 233–251. Warszawa: Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe 1975.
Stankowski J., Kuczyński W.: Fiz. Dielektr. Radiospektr.4, 249–255 (1966)
Pilawa B., Więckowski A.B.: Fuel76, 1173–1177 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilawa, B., Latocha, M., Buszman, E. et al. Effect of oxygen on spin-spin and spin-lattice relaxation in DOPA-melanin. Complexes with chloroquine and metal ions. Appl. Magn. Reson. 25, 105–111 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166970
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166970