Abstract
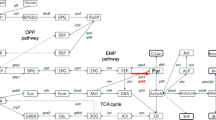
The Embden-Meyerhof (EM) or Entner-Doudoroff (ED) pathways of sugar degradation were analyzed in representative species of the hyperthermophilic archaeal genera Thermococcus, Desulfurococcus, Thermoproteus, and Sulfolobus, and in the hyperthermophilic (eu)bacterial genus Thermotoga. The analyses included (1) determination of 13C-labeling patterns by 1H- and 13C-NMR spectroscopy of fermentation products derived from pyruvate after fermentation of specifically 13C-labeled glucose by cell suspensions, (2) identification of intermediates of sugar degradation after conversion of 14C-labeled glucose by cell extracts, and (3) measurements of enzyme activities in cell extracts. Thermococcus celer and Thermococcus litoralis fermented 13C-glucose to acetate and alanine via a modified EM pathway (100%). This modification involves ADP-dependent hexokinase, 6-phosphofructokinase, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (GAP:FdOR). Desulfurococcus amylolyticus fermented 13C-glucose to acetate via a modified EM pathway in which GAP:FdOR replaces GAP-DH/phosphoglycerate kinase. Thermoproteus tenax fermented 13C-glucose to low amounts of acetate and alanine via simultaneous operation of the EM pathway (85%) and the ED pathway (15%). Aerobic Sulfolobus acidocaldarius fermented 13C-labeled glucose to low amounts of acetate and alanine exclusively via the ED pathway. The anaerobic (eu)bacterium Thermotoga maritima fermented 13C-glucose to acetate and lactate via the EM pathway (85%) and the ED pathway (15%). Cell extracts contained glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase, key enzymes of the conventional phosphorylated ED pathway, and, as reported previously, all enzymes of the conventional EM pathway. In conclusion, glucose was degraded by hyperthermophilic archaea to pyruvate either via modified EM pathways with different types of hexose kinases and GAP-oxidizing enzymes, by the nonphosphorylated ED pathway, or by a combination of both pathways. In contrast, glucose catabolism in the hyperthermophilic (eu)bacterium Thermotoga involves the conventional forms of the EM and ED pathways. The data are in accordance with various previous reports.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EM:
-
Embden-Meyerhof
- ED:
-
Entner-Doudoroff
- KDPG:
-
2-Keto-3-deoxy-6-phospho-gluconate
- KDG:
-
2-Keto-3-deoxygluconate
- DHAP:
-
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
- GAP-DH:
-
Glyceraldehehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GAP:FdOR:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase
- G-6-P:
-
Glucose-1-phosphate
- F-6-P:
-
Fructose-6-phosphate
- F-1-P:
-
Fructose-1-phosphate
- F-1,6-BP:
-
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- 1,3-BPG:
-
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
- 3-PG:
-
3-Phosphoglycerate
- DTE:
-
Dithioerythritol
- TIM:
-
Triosephosphate isomerase
References
Bartels M (1989) Glukoseabbau über einen modifizierten Entner- Doudoroff Weg bei dem thermoacidophilen Archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. PhD Thesis, Medizinische Fakultät, Universität Lübeck
Blöchl E, Burggraf S, Fiala G, Lauerer G, Huber R, Rachel R, Segerer A, Stetter KO, Völkl P (1995) Isolation, taxonomy and phylogeny of hyperthermophilic microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:9–16
Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Slesarev AI, Miroshnichenko ML, Svetlichnaya TP, Alekseev VA (1988) Characteristics of Desulfurococcus amylolyticus n. sp. — a new extremely thermophilic archaebacterium isolated from thermal springs of Kamchatka and Kunashir Island. Mikrobiologia 57:94–101
Bowien B, Schlegel HG (1972) Isolierung und Charakterisierung katabolischer Defektmutanten von Hydrogenomonas eutropha Stamm H 16. Arch Microbiol 87:221–234
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brock TD, Brock KM, Belly RT, Weiss RL (1972) Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Microbiol 84:54–68
Budgen N, Danson MJ (1986) Metabolism of glucose via a modified Entner-Doudoroff pathway in the thermophilic archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. FEBS Lett 196:207–210
Conrad R, Schlegel HG (1977) Influence of aerobic and phototrophic growth conditions on the distribution of glucose and fructose carbon into Entner-Doudoroff and Embden- Meyerhof pathways in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Gen Microbiol 101:277–290
Conway T (1992) The Entner-Doudoroff pathway: history, physiology and molecular biology. FEMS Microbiol Rev 103:1–28
Daniel RM, Danson MJ (1995) Did primitive microorganisms use nonheme iron proteins in place of NAD/P? J Mol Evol 40: 559–563
Danson MJ (1988) Archaebacteria: the comparative enzymology of their central metabolic pathways. Adv Microb Physiol 29:165–231
Danson MJ (1993) Central metabolism of the Archaea. In: Kates M, Kushner DJ, Matheson AT (eds) The biochemistry of Archaea (Archaebacteria). (New comprehensive biochemistry, vol 26). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–24
Danson MJ, Hough DW (1992) The enzymology of archaebacterial pathways of central metabolism. Biochem Soc Symp 58:7–21
De Rosa M, Gambacorta A, Nicolaus B, Giardina P, Poerio E, Buonocore V (1984) Glucose metabolism in the extreme thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biochem J 224:407–414
Fiala G, Stetter KO (1986) Pyrococcus furiosus sp. nov. represents a novel genus of marine heterotrophic archaebacteria growing optimally at 100° C. Arch Microbiol 145:56–61
Gottschalk G, Bender R (1972) D-Gluconate dehydratase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Methods Enzymol 90:283–287
Huber R, Langworthy TA, König H, Thomm M, Woese CR, Sleytr UB, Stetter KO (1986) Thermotoga maritima sp. nov. represents a new genus of unique extremely thermophilic eubacteria growing up to 90° C. Arch Microbiol 144:324–333
Kandler O (1993) Archaea (Archaebacteria). Prog Bot 54:1–24
Kengen SWM, Stams AJM (1994a) Formation of l-alanine as a reduced end product in a carbohydrate fermentation by the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. Arch Microbiol 161:168–175
Kengen SWM, Stams AJM (1994b) Growth and energy conservation in batch cultures of Pyrococcus furiosus. FEMS Microbiol Lett117:305–310
Kengen SWM, Luesink EJ, Stams AJM, Zehnder AJB (1993) Purification and characterization of an extremely thermostable b- glucosidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. Eur J Biochem 213:305–312
Kengen SWM, De Bok FAM, Van Loo N-D, Dijkema C, Stams AJM, De Vos WM (1994) Evidence for the operation of a novel Embden-Meyerhof pathway that involves ADP-dependent kinases during sugar fermentation by Pyrococcus furiosus. J Biol Chem 269:17537–17541 ai]Kengen SWM, Tuininga JE, De Bok FAM, Stams AJM, De Vos WM (1995) Purification and characterization of a novel ADPdependent glucokinase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Biol Chem 270:30453–30457
Leuschner C, Antranikian G (1995) Heat-stable enzymes from extremely thermophilic and hyperthermophilic microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:95–114
Mukund S, Adams MWW (1991) The novel tungsten-iron-sulfur protein of the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium, Pyrococcus furiosus, is an aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem 266:14208–14216
Mukund S, Adams MWW (1995) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ferredoxin oxidoreductase, a novel tungsten-containing enzyme with a potential glycolytic role in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Biol Chem 270:8389–8392
Neuner A, Jannasch HE, Belkin S, Stetter KO (1990) Thermococcus litoralis sp. nov.: a new species of extremely thermophilic marine archaebacteria. Arch Microbiol 153:205–207
Romano AH, Saier MH (1992) Evolution of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. I. Physiologic and organismic considerations. In: Mortlock RP (ed) The evolution of metabolic function. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 144–170
Sawyer MH, Baumann P, Baumann L, Berman SM, Cánovas JL (1977) Pathways of D-fructose catabolism in species of Pseudomonas. Arch Microbiol 112:49–55
Schäfer T, Schönheit P (1991) Pyruvate metabolism of the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Acetate formation from acetyl-CoA and ATP synthesis are catalyzed by an acetyl-CoA synthetase (ADP forming). Arch Microbiol 155:366–377
Schäfer T, Schönheit P (1992) Maltose fermentation to acetate, CO2 and H2 in the anaerobic hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: evidence for the operation of a novel sugar fermentation pathway. Arch Microbiol 158:188–202
Schäfer T, Schönheit P (1993) Gluconeogenesis from pyruvate in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: involvement of reactions of the Embden-Meyerhof pathway. Arch Microbiol 159:354–363
Schäfer T, Selig M, Schönheit P (1993) Acetyl-CoA synthetase (ADP forming) in archaea, a novel enzyme involved in acetate formation and ATP synthesis. Arch Microbiol 159:72–83
Schäfer G, Anemüller S, Moll R, Gleissner M, Schmidt CL (1994a) Has Sulfolobus an archaic respiratory system? Structure, function and genes of its components. Syst Appl Microbiol 16:544–555
Schäfer T, Xavier KB, Santos H, Schönheit P (1994b) Glucose fermentation to acetate and alanine in resting cell suspensions of Pyrococcus furiosus: proposal of a novel glycolytic pathway based on 13C labelling data and enzyme activities. FEMS Microbiol Lett 121:107–114
Schönheit P, Schäfer T (1995) Metabolism of hyperthermophiles. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:26–57
Schönheit P, Wäscher C, Thauer RK (1978) A rapid procedure for the purification of ferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum using polyethyleneimine. FEBS Lett 89:219–222
Schröder C, Selig M, Schönheit P (1994) Glucose fermentation to acetate, CO2 and H2 in the anaerobic hyperthermophilic eubacterium Thermotoga maritima: involvement of the Embden- Meyerhof pathway. Arch Microbiol 161:460–470
Selig M, Schönheit P (1994) Oxidation of organic compounds to CO2 with sulfur or thiosulfate as electron acceptor in the anaerobic hyperthermophilic archaea Thermoproteus tenax and Pyrobaculum islandicum proceeds via the citric acid cycle. Arch Microbiol 162:286–294
Siebers B, Hensel R (1993) Glucose catabolism of the hyperthermophilic archaeum Thermoproteus tenax. FEMS Microbiol Lett 111:1–8
Stetter KO, Fiala G, Huber G, Huber R, Segerer A (1990) Hyperthermophilic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 75:117–124
Tomlinson GA, Koch TK, Hochstein LI (1974) The metabolism of carbohydrates by extremely halophilic bacteria: glucose metabolism via a modified Entner-Doudoroff pathway. Can J Microbiol 20:1085–1091
Wächtershäuser G (1990) Evolution of the first metabolic cycles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:200–204
Weissbach A, Hurwitz J (1958) The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem 234:705–709
Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML (1990) Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal of the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4576–4579
Yu JP, Ladapo J, Whitman WB (1994) Pathway of glycogen metabolism in Methanococcus maripaludis. J Bacteriol 176:325–332
Zillig W, Stetter KO, Schäfer W, Janekovic D, Wunderl S, Holz I, Palm P (1981) Thermoproteales: a novel type of extremely thermoacidophilic anaerobic archaebacteria isolated from Islandic solfataras. Zentralbl Bakteriol Hyg C 2:205–227
Zillig W, Holz I, Janekovic D, Schäfer W, Reiter WD (1983) The archaebacterium Thermococcus celer represents a novel genus within the thermophilic branch of the archaebacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:88–94
Zwickl P, Fabry S, Bogedain C, Haas A, Hensel R (1990) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus woesei: characterization of the enzyme, cloning and sequencing of the gene, and expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 172:4329–4338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor A. Kröger on the occasion of his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selig, M., Xavier, K.B., Santos, H. et al. Comparative analysis of Embden-Meyerhof and Entner-Doudoroff glycolytic pathways in hyperthermophilic archaea and the bacterium Thermotoga. Arch Microbiol 167, 217–232 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356097
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356097