Abstract
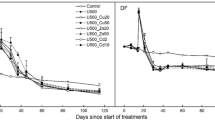
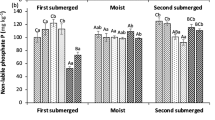
The effects of urinary chloride and nitrogen concentration and osmotic pressure on the nitrification of ammonium in a calcareous soil treated with cow urine were examined. Urinary chloride concentrations of up to 7.4 g L−1 had no effect on the rate of nitrification, as determined by the accumulation of soil nitrate. Osmotic stress, generated using a mixed salt solution, had an inhibitory effect on nitrification at soil osmotic pressures lower than or equal to −1.0 PMa. Nitrification was completely inhibited at a soil osmotic pressure of −2.6 MPa. Accumulation of nitrate after a lag phase of 18 days was noted in the −2.0 MPa soil osmotic pressure treatment, indicating some degree of adaptation or osmo-regulation within the nitrifying population at this stress level. High urine-N concentrations resulted in considerable nitrite accumulations and reduced nitrification activity through the effect of free ammonia. It is concluded that in most temperate grassland soils at near-neutral pH, urinary chloride and nitrogen are unlikely to reduce nitrification rates, except where urine-N concentrations exceed 16 g N L−1. Inhibition due to osmotic stress will be directly related to soil moisture status and may be particularly severe in dry, light-textured soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, A S, Singh, B R and Yanehiro, Y 1971 Ionic effects of salts on mineral nitrogen in an allophanic soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 35, 454–457.
Aleem M I H, Engel M S and Alexander M 1957 The inhibition of nitrification by ammonia. Bact. Proc. Soc. Am. Bacteriologists, p. 9
Anthonisen, A C, Loehr, R C, Parkasam, T B S and Srinath, E G 1976 Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. Journal of Water Pollution Control Fed. 48, 835–852.
Darrah, P R, Nye, P H and White, R E 1985 Modelling growth responses of soil nitrifiers to additions of ammonium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Plant and Soil 86, 425–439.
Darrah, P R, Nye, P H and White, R E 1987 The effect of high solute concentrations on nitrification rates in soil. Plant and Soil 97, 37–45.
Erh, K T, Elrick, D E, Thomas, R L and Corke, C T 1967 Dynamics of nitrification in soils using a miscible displacement technique. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 31, 383–389.
Harris R F 1981 Effect of water potential on microbial growth and activity. In Water Potential Relations in Soil Microbiology. Ed. D M Kral. pp 23–98 Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Special Public. No. 9.
Heilman, P 1975 Effect of added salts on nitrogen release and nitrate levels in forest soils of the Washington coastal area. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 39, 778–782.
Holland, P T and During, C 1977 Movement of nitrate-N and transformations of urea-N under field conditions. N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 20, 479–488.
Johnson, D D and Guenzi, W D 1963 Influence of salts on ammonium oxidation and carbon dioxide evolution from soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 27, 663–666.
Koops, H P, Böttcher, B, Möller, U C, Pommerening-Roser, A and Stehr, G 1991 Classification of eight new species of ammonia-oxidising bacteria: Nitrosomonas communis sp. nov., Nitrosomonas ureae sp. nov., Nitrosomonas aestuarii sp. nov., Nitrosomonas marina sp. nov., Nitrosomonas nitrosa sp. nov., Nitrosomonas eutropha sp. nov., Nitrosomonas oligotropha sp. nov., and Nitrosomonas halophila sp. nov. J. Gen. Microbiol. 137, 1689–1699.
McClung, G and Frankenberger, W T 1985 Soil nitrogen transformations as affected by salinity. Soil Science 139, 405–411.
McCormick, R W and Wolf, D C 1980 Effect of sodium chloride on carbon dioxide evolution, ammonification and nitrification in a Sassafras sandy loam. Soil Biol. Biochem. 12, 253–157.
Mexal, J, Fisher, J T, Osteryoung, J and Reid, C P P 1975 Oxygen availability in polyethylene glycol solution and its implications in plant-water relations. Plant Physiol. 55, 20–24.
Monreal, C, McGill, W B and Nyborg, M 1986 Spatial heterogeneity of substrates: Effects on hydrolysis, immobilization and nitrification of urea-N. Can. J. Soil Sci. 66, 499–511.
Morrill, L G and Dawson, J E 1962 Growth rates of nitrifying chemoautotrophs in soil. J. Bacteriol. 83, 205–206.
Morrill, L G and Dawson, J E 1967 Patterns observed for the oxidation of ammonium to nitrate by soil organisms. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 31, 757–760.
Pang, P C, Hedlin, R A and Cho, C M 1973 Transformation and movement of band-applied urea, ammonium sulphate and ammonium hydroxide during incubation in several Manitoba soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 53, 331–341.
Quin, B F 1977 The fate of sheep urine-nitrogen on surface-irrigated pasture in Canterbury. N.Z. Soil News 25, 140–143.
Rees, M K 1968 Effect of chloride on oxidation of hydroxylamine by Nitrosomonas europaea cells. J. Bacteriol. 95, 243–244.
Robinson, J B 1963 Nitrification in a New Zealand grassland soil. Plant and Soil 19, 173–183.
Roseburg, R J, Christensen, N W and Jackson, T L 1986 Chloride, soil solution osmotic potential and soil pH effects on nitrification. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 941–945.
Scott, W J 1957 Water relations of food spoilage microorganisms. Adv. Food Res. 7, 83–127.
Sindhu, M A and Cornfield, A H 1967 Comparative effects of varying levels of chlorides and sulphates of sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium on ammonification and nitrification during incubation of soil. Plant and Soil 27, 468–472.
Westerman, R L and Tucker, T C 1974 Effects of salts and salts plus nitrogen-15 labelled ammonium chloride on mineralization of soil nitrogen, nitrification and immobilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 38, 602–605.
Wickramasinghe, K N, Rodgers, G A and Jenkinson, D S 1985 Nitrification in acid tea soils and a neutral grassland soil: effects of nitrification inhibitors and inorganic salts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 17, 249–252.
Yeo, A R and Flowers, T J 1984 Non-osmotic effects of polyethylene glycol upon sodium transport and Na-K selectivity by rice roots. Plant Physiol. 75, 298–303.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monaghan, R.M., Barraclough, D. Some chemical and physical factors affecting the rate and dunamics of nitrification in urine-affected soil. Plant Soil 143, 11–18 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009124
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009124