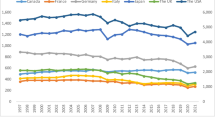
Abstract
The study examines the asymmetric effect of electricity consumption on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by analyzing end-user groups. In this context, the study focuses on the USA, which is the largest economy. The study includes the most available monthly data from January 1973 to November 2021, performs nonlinear quantile approaches as Granger causality-in-quantiles, nonparametric causality-in-quantiles, and quantile-on-quantile regression (QQR). Besides, quantile regression (QR) approach is used for robustness checks. The empirical results show that (i) correlation relationship between the electricity consumption and CO2 emissions changes according to the terms; (ii) there are generally causality effects in quantiles excluding some lower (0.05, 0.25), middle (0.70, 0.75), and high (0.95) quantiles, while the results for end-user groups vary; (iii) similarly, there is nonparametric causality from the end-user electricity consumption indicators to the CO2 emissions for the mean (return) and the variance (volatility) in most of the quantiles excluding some; (iv) the effects of the electricity consumption indicators on the CO2 emissions are higher in lower quantiles; (v) the QR results show the robustness of the QQR results. Overall, the effects of the electricity consumption indicators on the CO2 emissions are asymmetric and change according to the terms, quantiles, mean, variance, and end-user groups. Furthermore, policy implications are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) at https://www.eia.gov/totalenergy/data/monthly.
References
Abbasi KR, Hussain K, Abbas J, Adedoyin FF, Shaikh PA, Yousaf H, Muhammad F (2021) Analyzing the role of industrial sector’s electricity consumption, prices, and GDP: a modified empirical evidence from Pakistan. Aims Energy 9(1):29–49
Adebayo TS (2022a) Renewable energy consumption and environmental sustainability in Canada: does political stability make a difference? Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20008-4
Adebayo TS (2022b) Environmental consequences of fossil fuel in Spain amidst renewable energy consumption: a new insights from the wavelet-based Granger causality approach. Int J Sust Dev World 3(4):1–14
Adebayo TS, AbdulKareem HK, Kirikkaleli D, Shah MI, Abbas S (2022) CO2 behavior amidst the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy development. Renew Energy 189:492–501
Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Adeshola I (2020) Determinants of CO2 emissions in emerging markets: an empirical evidence from MINT economies. Int J Renew Energy Dev 9(3):411–422
Adebayo TS, Udemba EN, Ahmed Z, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Determinants of consumption-based carbon emissions in Chile: an application of non-linear ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(32):43908–43922
Bal DP, Patra SK, Mohanty S (2022) Impact of sectoral decompositions of electricity consumption on economic growth in India: evidence from SVAR framework. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19352-2
Balcılar M, Gupta R, Pierdzioch C (2016) Does uncertainty move the gold price? New evidence from a nonparametric causality-in-quantiles test. Resour Policy 49:74–80
Bhattacharya M, Paramati SR, Öztürk İ, Bhattacharya S (2016) The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: evidence from top 38 countries. Appl Energy 162:733–741
BP (2022) Energy data. https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html, Mar 13, 2022
Broock WA, Scheinkman JA, Dechert WD, LeBaron B (1996) A test for independence based on the correlation dimension. Economet Rev 15(3):197–235
Chang CH, Chen ZB, Huang SF (2022) Forecasting of high-resolution electricity consumption with stochastic climatic covariates via a functional time series approach. Appl Energy 309:118418
Cheng Y, Yao X (2021) Carbon intensity reduction assessment of renewable energy technology innovation in China: a panel data model with cross-section dependence and slope heterogeneity. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 135:110157
Cheng K, Hsueh HP, Ranjbar O, Wang MC, Chang T (2021) Urbanization, coal consumption and CO2 emissions nexus in china using bootstrap Fourier Granger causality test in quantiles. Lett Spat Resour Sci 14(1):31–49
Chien F, Hsu CC, Öztürk İ, Sharif A, Sadiq M (2022) The role of renewable energy and urbanization towards greenhouse gas emission in top Asian countries: evidence from advance panel estimations. Renew Energy 186:207–216
Dickey DA, Fuller WA (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J Am Stat Assoc 74(366a):427–431
EIA (2022) Monthly energy review. https://www.eia.gov/totalenergy/data/monthly, Mar 10, 2022
Fernández-Macho J (2012) Wavelet multiple correlation and cross-correlation: a multiscale analysis of euro zone stock markets. Physica A 391(4):1097–1104
Kartal MT (2022) The role of consumption of energy, fossil sources, nuclear energy, and renewable energy on environmental degradation in top-five carbon producing countries. Renew Energy 184:871–880
Kartal MT, Kılıç Depren S, Ayhan F, Depren Ö (2022) Impact of renewable and fossil fuel energy consumption on environmental degradation: evidence from USA by nonlinear approaches. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol Forthcoming. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2022.2087115
Kılıç Depren S, Kartal MT, Ertuğrul HM, Depren Ö (2022) The role of data frequency and method selection in electricity price estimation: comparative evidence from Turkey in pre-pandemic and pandemic periods. Renew Energy 186:217–225
Kirikkaleli D, Güngör H, Adebayo TS (2022) Consumption-based carbon emissions, renewable energy consumption, financial development and economic growth in Chile. Bus Strateg Environ 31(3):1123–1137
Koenker R (2005) Quantile regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kwiatkowski D, Phillips PC, Schmidt P, Shin Y (1992) Testing the null hypothesis of stationarity against the alternative of a unit root: how sure are we that economic time series have a unit root? J Econ 54(1–3):159–178
Li D, Huang G, Zhu S, Chen L, Wang J (2021a) How to peak carbon emissions of provincial construction industry? Scenario analysis of Jiangsu province. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 144:110953
Li R, Woo CK, Cox K (2021b) How price-responsive is residential retail electricity demand in the US? Energy 232:120921
Narayan PK, Narayan S, Prasad A (2008) A structural VAR analysis of electricity consumption and real GDP: evidence from the G7 countries. Energy Policy 36(7):2765–2769
Oliveira H, Moutinho V (2021) Renewable energy, economic growth and economic development nexus: a bibliometric analysis. Energies 14(15):4578
Rahaman M, Hossain M, Chen S (2022) The impact of foreign direct investment, tourism, electricity consumption, and economic development on CO2 emissions in Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(25):37344–37358
Rehman A, Ma H, Öztürk İ, Radulescu M (2022) Revealing the dynamic effects of fossil fuel energy, nuclear energy, renewable energy, and carbon emissions on Pakistan’s economic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19317-5
Sanquist TF, Orr H, Shui B, Bittner AC (2012) Lifestyle factors in US residential electricity consumption. Energy Policy 42:354–364
Santamouris M, Cartalis C, Synnefa A, Kolokotsa D (2015) On the impact of urban heat island and global warming on the power demand and electricity consumption of buildings-a review. Energy and Buildings 98:119–124
Sharif A, Mishra S, Sinha A, Jiao Z, Shahbaz M, Afshan S (2020) The renewable energy consumption-environmental degradation nexus in top-10 polluted countries: fresh insights from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Renew Energy 150:670–690
Sharif A, Bhattacharya M, Afshan S, Shahbaz M (2021) Disaggregated renewable energy sources in mitigating CO2 emissions: new evidence from the USA using quantile regressions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(41):57582–57601
Sim N, Zhou H (2015) Oil prices, US Stock Return, and the dependence between their quantiles. J Bank Finance 55:1–8
Soytaş MA, Ertuğrul HM, Ulussever T (2020) Nonlinear excess demand model for electricity price prediction. Economic Research Forum Working Papers, No. 1449. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mehmet-Soytas/publication/347590730_Nonlinear_Excess_Demand_Model_for_Electricity_Price_Prediction/links/5ff1e0b345851553a015d9d8/Nonlinear-Excess-Demand-Model-for-Electricity-Price-Prediction.pdf
Tonkovic MP, Hussain SA (2017) Residential and non-residential electricity dynamics. Energy Econ 64:262–271
Troster V (2018) Testing for Granger-causality in quantiles. Economet Rev 37(8):850–866
Ummalla M, Goyari P (2021) The impact of clean energy consumption on economic growth and CO2 emissions in BRICS countries: does the environmental Kuznets curve exist? J Public Aff 21(1):e2126
Wilson B (2013) Urban form and residential electricity consumption: evidence from Illinois, USA. Landsc Urban Plan 115:62–71
World Bank (2022) GDP current US$. https://data.worldbank.org, Mar 13, 2022
Yuping L, Ramzan M, Xincheng L, Murshed M, Awosusi AA, Bah SI, Adebayo TS (2021) Determinants of carbon emissions in Argentina: the roles of renewable energy consumption and globalization. Energy Rep 7:4747–4760
Zhan Z, Ali L, Sarwat S, Godil DI, Dinca G, Anser MK (2021) A step towards environmental mitigation: do tourism, renewable energy and institutions really matter? A QARDL Approach. Sci Total Environ 778:146209
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mustafa Tevfik Kartal: the design of the study, conceptualization; methodology; data collection; econometric analysis; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing; Uzair Ali: writing—review and editing; Zhanar Nurgazina: writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors are willing to permit the journal to publish the article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kartal, M.T., Ali, U. & Nurgazina, Z. Asymmetric effect of electricity consumption on CO2 emissions in the USA: analysis of end-user electricity consumption by nonlinear quantile approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 83824–83838 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21715-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21715-8