Abstract
Purpose
The diuretic effect of tolvaptan is largely blood level-dependent although it does exhibit interindividual differences according to cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A5 genotype. This study aimed to investigate the pharmacokinetic relationship between plasma tolvaptan and its monohydroxylate enantiomers and the factors affecting their metabolism in heart failure patients.
Methods
Japanese heart failure patients (n = 88) receiving oral tolvaptan (median dosage 7.5 mg/day) were enrolled. Blood samples were collected prior to the dosing on day 6 or later after first administration to determine the plasma concentrations of tolvaptan and its monohydroxylate enantiomers. Gene polymorphisms of CYP3A5, carbonyl reductase (CBR) 1/3, and ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member (ABCB) 1 were analyzed for their impact on tolvaptan pharmacokinetics. Serum laboratory test values and concomitant use of amiodarone were evaluated as factors related to tolvaptan metabolism.
Results
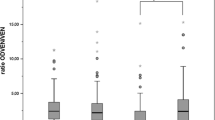
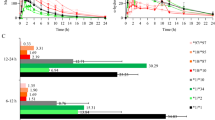
The median of the sum of the 5S- and 5R-tolvaptan plasma concentrations was 48.9 (range, 15.3–100) ng/mL. CYP3A5 genotypes significantly affected the concentration ratio of all enantiomeric metabolites to tolvaptan, while the other metabolic-related gene polymorphisms had no influence. A negative correlation was found between serum albumin and the enantiomeric ratio of tolvaptan and monohydroxylate DM-4111. Concomitant use of amiodarone increased the plasma levels of whole tolvaptan but significantly decreased the metabolic ratios of 5R-tolvaptan. 5S-tolvaptan was selectively synthesized from ketone MOP-21826 by CBR1 with a substantially smaller reaction velocity compared to tolvaptan monohydroxylation by CYP3A4/5.
Conclusion
This study clarified the racemic impact of CYP3A5 genotypes on tolvaptan metabolism. Amiodarone may stereoselectively interact with R-forms rather than S-forms of tolvaptan.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
- ABCB:
-
ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member
- EDTA:
-
Ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid
- LC-MSMS:
-
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- CBR:
-
Carbonyl reductase
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- Km:
-
Michaelis constant
- Vmax:
-
Maximum velocity
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- OATP:
-
Organic anion transporter
References
Yamamura Y, Nakamura S, Itoh S, Hirano T, Onogawa T, Yamashita T, Yamada Y, Tsujimae K, Aoyama M, Kotosai K, Ogawa H, Yamashita H, Kondo K, Tominaga M, Tsujimoto G, Mori T (1998) OPC-41061, a highly potent human vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist: pharmacological profile and aquaretic effect by single and multiple oral dosing in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287(3):860–867
Fukunami M, Matsuzaki M, Hori M, Izumi M (2011) Efficacy and safety of tolvaptan in heart failure patients with sustained volume overload despite the use of conventional diuretics: a phase III open-label study. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 25:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-011-6348-y
Sakaida I, Yamashita S, Kobayashi T, Komatsu M, Sakai T, Komorizono Y, Okada M, Okita K (2013) Efficacy and safety of a 14-day administration of tolvaptan in the treatment of patients with ascites in hepatic oedema. J Int Med Res 41(3):835–847. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060513480089
Kinugawa K, Imamura T, Komuro I (2013) Experience of a vasopressin receptor antagonist, tolvaptan, under the unique indication in Japanese heart failure patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 94(4):449–451. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2013.147
Okabe T, Yakushiji T, Igawa W, Ono M, Kido T, Ebara S, Yamamoto MH, Saito S, Hoshimoto K, Amemiya K, Isomura N, Araki H, Ochiai M (2015) The efficacy of tolvaptan in congestive heart failure patients with and without hypoalbuminemia: a pilot study. Cardiovasc Ther 33(5):275–281
Kinugawa T, Sato N, Inomata T, Yasuda M, Shibasaki Y, Shimakawa T (2018) Novel risk score efficiently prevents hypernatremic event by tolvaptan in patients with heart failure. Circ J 25:1344–1350. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.CJ-17-0986
Gibson A, Hammond S, Jaruthamsophon K, Roth S, Mosedale M, Naisbitt DJ (2020) Tolvaptan- and tolvaptan-metabolite-responsive T cells in patients with drug-induced liver injury. Chem Res Toxicol 16(33):2745–2748. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00328
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2013) FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA limits duration and usage of Samsca (tolvaptan) due to possible liver injury leading to organ transplant or death. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm350062.htm. Accessed 6 May 2022
Kim SR, Hasunuma T, Sato O, Okada T, Kondo M, Azuma J (2011) Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of tolvaptan, a novel, oral, selective nonpeptide AVP V2-receptor antagonist: results of single- and multiple-dose studies in healthy Japanese male volunteers. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 25(Suppl 1):5–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-011-6299-3
Mazzarino M, Buccilli V, de la Torre X, Fiacco I, Palermo A, Ughi D, Botrè F (2017) Characterization of the phase I and phase II metabolic profile of tolvaptan by in vitro studies and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry profiling: relevance to doping control analysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 145(25):555–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.06.054
Hoshikawa K, Naito T, Akutsu S, Saotome M, Maekawa Y, Kawakami J (2020) Impact of CYP3A5 genotype on tolvaptan pharmacokinetics and their relationships with endogenous markers of CYP3A activity and serum sodium level in heart failure patients. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 126(4):353–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.13355
Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing (2012) Australian public assessment report for tolvaptan. https://www.tga.gov.au/sites/default/files/auspar-tolvaptan-180209121004.pdf. Accessed 6 May 2022
Shoaf SE, Ohzone Y, Ninomiya S, Furukawa M, Bricmont P, Kashiyama E, Mallikaarjun S (2011) In vitro P-glycoprotein interactions and steady-state pharmacokinetic interactions between tolvaptan and digoxin in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 51:761–769. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091270010376193
Slizgi JR, Lu Y, Brouwer KR, St Claire RL, Freeman KM, Pan M, Brock WJ, Brouwer KL (2016) Inhibition of human hepatic bile acid transporters by tolvaptan and metabolites: contributing factors to drug-induced liver injury? Toxicol Sci 149(1):237–250. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfv231
Abelö A, Andersson TB, Antonsson M, Naudot AK, Skånberg I, Weidolf L (2000) Stereoselective metabolism of omeprazole by human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos 28(8):966–972
Hayakawa I, Atarashi S, Yokohama S, Imaura M, Sakano K, Furukawa M (1986) Synthesis and antibacterial activities of optically active ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 29(1):163–164. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.29.1.163
Gillard M, Van Der Perren C, Moguilevsky N, Massingham R, Chatelain P (2002) Binding characteristics of cetirizine and levocetirizine to human H (1) histamine receptors: contribution of Lys (191) and Thr (194). Mol Pharmacol 61(2):391–399. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.61.2.391
Monti JM, Pandi-Perumal SR (2007) Eszopiclone: its use in the treatment of insomnia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 3(4):441–453
Takahashi H, Kashima T, Nomizo Y, Muramoto N, Shimizu T, Nasu K, Kubota T, Kimura S, Echizen H (1998) Metabolism of warfarin enantiomers in Japanese patients with heart disease having different CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 63(5):519–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-9236(98)90103-5
Yamazaki H, Shimada T (1997) Human liver cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the 7-hydroxylation of R- and S-warfarin enantiomers. Biochem Pharmacol 54(11):1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-2952(97)00304-3
Li F, Howard KD, Myers MJ (2017) Influence of P-glycoprotein on the disposition of fexofenadine and its enantiomers. J Pharm Pharmacol 69(3):274–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12687
Furukawa M, Yamasaki Y, Hirano Y, Umehara K (2014) Enantioselective analysis of tolvaptan in rat and dog sera by high-performance liquid chromatography and application to pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B 965(15):112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.06.007
Akutsu S, Naito T, Hoshikawa K, Saotome M, Maekawa Y, Kawakami J (2020) An enantiomeric quantitative LC-MS/MS method for tolvaptan and its monohydroxylates in human plasma using a reversed-phase separation procedure. J Pharm Biomed Anal 180:113061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.113061
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2018) Bioanalytical method validation guidance for industry. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry. Accessed 6 May 2022.
Lal S, Sandanaraj E, Wong ZW, Ang PCS, Wong NS, Lee EJ, Chowbay B (2008) CBR1 and CBR3 pharmacogenetics and their influence on doxorubicin disposition in Asian breast cancer patients. Cancer Sci 99(10):2045–2054. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00903.x
Lombraña AQ, Li N, Del Solar V, Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Blanco JG (2018) CBR1 rs9024 genotype status impacts the bioactivation of loxoprofen in human liver. Biopharm Drug Dispos 39(6):315–318. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.2135
Hoshikawa K, Naito T, Saotome M, Maekawa Y, Kawakami J (2019) Validated liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous quantitation of tolvaptan and its five major metabolites in human plasma. Ann Clin Biochem 56(3):387–396. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004563219827045
Wirth H, Wermuth B (1992) Immunohistochemical localization of carbonyl reductase in human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 40(12):1857–1863. https://doi.org/10.1177/40.12.1453004
Zanger UM, Schwab M (2013) Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacol Ther 138(1):103–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.12.007
Breyer-Pfaff U, Nill K (2004) Carbonyl reduction of naltrexone and dolasetron by oxidoreductases isolated from human liver cytosol. J Pharm Pharmacol 56(12):1601–1606. https://doi.org/10.1211/0022357045020
Malátková P, Sokolová S, Chocholoušová Havlíková L, Wsól V (2016) Carbonyl reduction of warfarin: identification and characterization of human warfarin reductases. Biochem Pharmacol 109:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.025
Akamine Y, Miura M, Komori H, Tamai I, Ieiri I, Yasui-Furukori N, Uno T (2015) The change of pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine enantiomers through the single and simultaneous grapefruit juice ingestion. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 30(5):352–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dmpk.2015.06.005
Honjo H, Uwai Y, Aoki Y, Iwamoto K (2011) Stereoselective inhibitory effect of flurbiprofen, ibuprofen and naproxen on human organic anion transporters hOAT1 and hOAT3. Biopharm Drug Dispos 32:518–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.779
Kawase A, Yamamoto T, Egashira S, Iwaki M (2016) Stereoselective inhibition of methotrexate excretion by glucuronides of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs via multidrug resistance proteins 2 and 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 356:366–374. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.115.229104
Singh SN, Fletcher RD, Fisher SG, Singh BN, Lewis HD, Deedwania PC, Massie BM, Colling C, Lazzeri D (1995) Amiodarone in patients with congestive heart failure and asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmia. Survival trial of antiarrhythmic therapy in congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 333(2):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199507133330201
Singh BN, Singh SN, Reda DJ, Tang XC, Lopez B, Harris CL, Fletcher RD, Sharma SC, Atwood JE, Jacobson AK, Lewis HD Jr, Raisch DW, Ezekowitz MD (2005) Amiodarone versus sotalol for atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 352(18):1861–1872. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa041705
Acknowledgements
5R- and 5S-tolvaptan, DM-4110 (4R5R/4S5S-diols), DM-4111 (4S5R/4R5S-diols), and DM-4119 (3S5R/3R5S-diols) were generously provided by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Funding
This study was performed with the support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number JP19H00346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the design of this study. SA and KH conducted data collection. SA analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript with advice from YM. All authors contributed substantially to its revision. All authors read and approved the final draft for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Ethics Committee of Hamamatsu University School of Medicine approved the study protocol (20–105). This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and Medical and Health Research Involving Human Subjects in Japan.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from each of the participating individuals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akutsu, S., Mino, Y., Naito, T. et al. Stereoselective interaction of tolvaptan with amiodarone under racemic metabolic impact by CYP3A5 genotypes in heart failure patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 78, 1311–1320 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-022-03341-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-022-03341-y