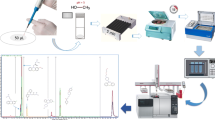
Abstract
Histidine (His) is an essential amino acid that plays an important biological role and associated with various pathological conditions. A simple and reliable method for the determination of endogenous histidine in human saliva was optimized and validated. The analyte was separated from the saliva matrix by cation exchange chromatography and detected fluorimetrically (λex/λem = 360/440 nm) after online, specific post-column derivatization (PCD) reaction with o-phthalaldehyde. The chemical and instrumental variables of the post-column reaction were optimized using Box–Behnken experimental design to achieve maximum sensitivity. Method validation was carried out employing the total-error concept. Histidine could be analyzed reliably in the range of 0.5–5.0 μΜ, with an LOD (S/N = 3) of 50 nM. Monte Carlo simulations and capability analysis were used to investigate the ruggedness of the PCD reaction. The sampling strategy, sample preparation and stability were also investigated. Seventeen saliva samples were successfully analyzed with histidine levels being in the range of 2.7–19.5 μΜ.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
High-pressure liquid chromatography
- PCD:
-
Post-column derivatization
- His:
-
Histidine
- OPA:
-
o-Phthalaldehyde
- BISM:
-
Binary inlet static mixer
- LOD/LOQ:
-
Limits of detection/quantitation
- β-ΕΤΙ:
-
β-Expectation tolerance intervals
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BBD:
-
Box–Behnken design
- LoF:
-
Lack of fit
- LLOQ:
-
Lower limit of quantitation
References
Acuña I, Ruiz A, Cerdó T et al (2021) Rapid and simultaneous determination of histidine metabolism intermediates in human and mouse microbiota and biomatrices. BioFactors. https://doi.org/10.1002/BIOF.1766
Alevridis A, Tsiasioti A, Zacharis CK, Tzanavaras PD (2020) Fluorimetric method for the determination of histidine in random human urine based on zone fluidics. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES25071665
Balci N, Kurgan Ş, Çekici A et al (2021) Free amino acid composition of saliva in patients with healthy periodontium and periodontitis. Clin Oral Investig 25:4175–4183. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00784-021-03977-7/TABLES/3
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP et al (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76:965–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.019
Cheng F, Wang Z, Huang Y et al (2015) Investigation of salivary free amino acid profile for early diagnosis of breast cancer with ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta 447:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCA.2015.05.008
Derringer G, Suich R (1980) Simultaneous optimization of several response variables. J Qual Technol 12:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224065.1980.11980968
Elmongy H, Abdel-Rehim M (2016) Saliva as an alternative specimen to plasma for drug bioanalysis: a review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 83:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRAC.2016.07.010
Emekli-Alturfan E, Kasikci E, Alturfan AA et al (2009) Effect of sample storage on stability of salivary glutathione, lipid peroxidation levels, and tissue factor activity. J Clin Lab Anal 23:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/JCLA.20296
FDA (2018) Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance. In: Food Drug Adm. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry. Accessed 11 Jan 2021
Ferreira SLC, Bruns RE, Ferreira HS et al (2007) Box-Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal Chim Acta 597:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.07.011
Gal JY, Fovet Y, Adib-Yadzi M (2001) About a synthetic saliva for in vitro studies. Talanta 53:1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(00)00618-4
Håkanson R, Rönnberg AL, Sjölund K (1974) Improved fluorometric assay of histidine and peptides having NH2-terminal histidine using o-Phthalaldehyde. Anal Biochem 59:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(74)90014-1
Hibbert DB (2012) Experimental design in chromatography: a tutorial review. J Chromatogr B 910:2–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.01.020
Holeček M (2020) Histidine in health and disease: metabolism, physiological importance, and use as a supplement. Nutr 12:848. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU12030848
Hubert P, Nguyen-Huu JJ, Boulanger B et al (2003) Validation of quantitative analytical procedure, harmonization of approaches. STP Pharma Prat 13:101–138
Hubert P, Nguyen-Huu JJ, Boulanger B et al (2004) Harmonization of strategies for the validation of quantitative analytical procedures: a SFSTP proposal—part I. J Pharm Biomed Anal 36:579–586
Hubert P, Nguyen-Huu J-J, Boulanger B et al (2007) Harmonization of strategies for the validation of quantitative analytical procedures: a SFSTP proposal—part III. J Pharm Biomed Anal 45:82–96
Khurshid Z, Najeeb S, Mali M et al (2017) Histatin peptides: pharmacological functions and their applications in dentistry. Saudi Pharm J 25:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSPS.2016.04.027
Kim D, Mun S, Lee J et al (2018) Proteomics analysis reveals differential pattern of widespread protein expression and novel role of histidine-rich glycoprotein and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Biol Macromol 109:704–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2017.12.075
Kugimiya A, Fujikawa A, Jiang X et al (2020) Microfluidic paper-based analytical device for histidine determination. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 192:812–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12010-020-03365-Z/FIGURES/7
Lee Y-H, Wong DT (2009) Saliva: an emerging biofluid for early detection of diseases. Am J Dent 22:241–248
López-Grío S, Torres-Lapasió JR, Baeza-Baeza JJ, García-Alvarez-Coque MC (2000) Micellar liquid chromatographic separation of amino acids using pre- and post-column o-phthalaldehyde/N-acetylcysteine derivatization. Anal Chim Acta 418:153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)00965-X
Mandur J, Budman H (2014) Robust optimization of chemical processes using Bayesian description of parametric uncertainty. J Process Control 24:422–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2013.10.004
Marvin RK, Saepoo MB, Ye S et al (2017) Salivary protein changes in response to acute stress in medical residents performing advanced clinical simulations: a pilot proteomics study. Biomarkers 22:372–382. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750X.2017.1279215
Melguizo-Rodríguez L, Costela-Ruiz VJ, Manzano-Moreno FJ et al (2020) Salivary biomarkers and their application in the diagnosis and monitoring of the most common oral pathologies. Int J Mol Sci 21:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21145173
Melino S, Santone C, Di Nardo P, Sarkar B (2014) Histatins: salivary peptides with copper(II)- and zinc(II)-binding motifs. FEBS J 281:657–672. https://doi.org/10.1111/FEBS.12612
Nakamura Y, Kodama H, Satoh T, Adachi K, Watanabe S, Yokote Y, Sakagami H (2010) Diurnal changes in salivary amino acid concentrations. In Vivo (brooklyn) 24:837–842
Ngamchuea K, Batchelor-McAuley C, Compton RG (2017a) Rapid method for the quantification of reduced and oxidized glutathione in human plasma and saliva. Anal Chem 89:2901–2908. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.ANALCHEM.6B04186/SUPPL_FILE/AC6B04186_SI_001.PDF
Ngamchuea K, Chaisiwamongkhol K, Batchelor-Mcauley C, Compton RG (2017b) Chemical analysis in saliva and the search for salivary biomarkers—a tutorial review. Analyst 143:81–99. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AN01571B
Razavi F, Khajehsharifi H (2021) A colorimetric paper-based sensor with nanoporous SBA-15 for simultaneous determination of histidine and cysteine in urine samples. Chem Pap 757(75):3401–3410. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11696-021-01548-4
Reuven Y, Rubinstein DPK (2017) Simulation and the monte carlo method. Wiley
Rigas PG (2012) Review: liquid chromatography—post-column derivatization for amino acid analysis: strategies, instrumentation, and applications. Instrum Sci Technol 40:161–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/10739149.2011.651669
Rigas PG (2013) Post-column labeling techniques in amino acid analysis by liquid chromatography Amino Acid Analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:7957–7992. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00216-013-7127-3/FIGURES/4
Salivette Salivette - Hygienic saliva collection for diagnosis and monitoring. In: sarstedt AG. https://www.sarstedt.com/fileadmin/user_upload/99_Broschueren/Englisch/156_Salivette_GB_0813.pdf
Scalise M, Galluccio M, Console L et al (2018) The Human SLC7A5 (LAT1): the intriguing histidine/large neutral amino acid transporter and its relevance to human health. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCHEM.2018.00243
Soraya GV, Abeyrathne CD, Buffet C et al (2019) (2019) Ultrasensitive and label-free biosensor for the detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein II in saliva. Sci Reports 91(9):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53852-5
Stampina E, Tsiasioti A, Klimatsaki K et al (2021) Determination of histidine in human serum and urine by cation exchange chromatography coupled to selective on-line post column derivatization. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCHROMB.2021.122697
Tan SP, Brown SB, Griffiths CEM et al (2017) Feeding filaggrin: effects of L-histidine supplementation in atopic dermatitis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 10:403–411. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S146760
Tsiasioti A, Tzanavaras PD (2021) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using zone fluidics and fluorimetric detection. Talanta 222:121559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121559
Tsiasioti A, Andreou A, Tzanavaras PD (2020a) Selective reaction of homocysteine with o-phthalaldehyde under flow conditions in highly alkaline medium: fluorimetric determination using zone fluidics. Luminescence 35:1402–1407. https://doi.org/10.1002/BIO.3904
Tsiasioti A, Zacharis CK, Tzanavaras PD, Zotou AS (2020b) Study of the oxidative forced degradation of glutathione in its nutraceutical formulations using zone fluidics and green liquid chromatography. Separations 7:16. https://doi.org/10.3390/SEPARATIONS7010016
Wang Y, Zhao Z, Qin J et al (2020) Rapid in situ analysis of l-histidine and α-lactose in dietary supplements by fingerprint peaks using terahertz frequency-domain spectroscopy. Talanta. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2019.120469
Wu X, Huang J, Zhang C, Kang X (2021) Nanofibers comprising polystyrene and zinc acetate 2 for extraction of salivary histidine prior to its determination by HPLC-DAD. Anal Sci. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.21P134
Yamaguchi H, Nakata K, Tatsumi M et al (2019) Development of a novel l-histidine assay method using histamine dehydrogenase and a stable mutant of histidine decarboxylase. Anal Biochem 570:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AB.2018.12.017
Yao Z, Liu H, Liu Y et al (2020) Fluorimetric determination of histidine by exploiting its inhibitory effect on the oxidation of thiamine by cobalt-containing Prussian Blue nanocubes. Microchim Acta 187:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00604-019-3930-7/TABLES/2
Yoshimura T, Kamataki T, Miura T (1990) Difference between histidine and histamine in the mechanistic pathway of the fluorescence reaction with ortho-phthalaldehyde. Anal Biochem 188:132–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(90)90540-P
Zacharis CK, Tzanavaras PD (2013) Liquid chromatography coupled to on-line post column derivatization for the determination of organic compounds: a review on instrumentation and chemistries. Anal Chim Acta 798:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.07.032
Zhang CZ, Cheng XQ, Li JY et al (2016) Saliva in the diagnosis of diseases. Int J Oral Sci 83(8):133–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijos.2016.38
Zuman P (2004) Reactions of orthophthalaldehyde with nucleophiles. Chem Rev 104:3217–3238. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0304424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Research involving human participants, their data or biological material
All human participants in this study were members of the Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry of the Department of Chemistry and donated saliva samples on a voluntary basis. They were informed in detail about the non-medical nature of the work and provided written consent.
Informed consent
All human volunteers participating in this research were informed and provided written consent to participate in the study, including publication of the results.
Additional information
Handling editor: D. Tsikas.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gkantiri, AM., Tsiasioti, A., Zacharis, C.K. et al. HPLC method with post-column derivatization for the analysis of endogenous histidine in human saliva validated using the total-error concept. Amino Acids 54, 399–409 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-022-03135-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-022-03135-7