Abstract
Background
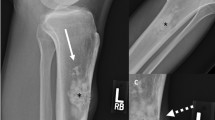
Resecting non-palpable soft tissue tumors presents a unique challenge, particularly with recurrent disease in which surrounding tissue has been surgically manipulated and often irradiated. SAVI SCOUT® is a radar-based localization device that was developed for breast tumor localization and was recently FDA-approved for localization of soft tissue tumors. Application of this technology to soft tissue sarcoma has not been previously reported.
Methods
We assembled a single-institution retrospective case series of patients with trunk and extremity sarcomas resected by five sarcoma surgeons using SAVI SCOUT® from December 2018 to May 2020. Reflectors were placed preoperatively using image-guidance, and the radar detector was used intraoperatively to localize the target lesion. Clinical variables were abstracted from the electronic medical record including treatment history, pathology, and early oncologic outcomes. Using a focused review, we compared margin status and recurrence rates with previously published cohorts.
Results
Ten SAVI SCOUT®-localized sarcoma resections were performed. Eight were for locally recurrent disease, of which seven (83%) had prior radiation. The remaining lesions became non-palpable after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. SAVI SCOUT® facilitated resection in all cases with a margin-negative resection rate (77%) comparable to prior cohorts. In this high-risk population with a median follow-up of 14 months, only one patient recurred locally 7.5 months after SAVI SCOUT®-localized resection, requiring re-resection.
Conclusion
SAVI SCOUT® technology facilitated resection of non-palpable recurrent sarcoma of the trunk and extremities in all ten cases attempted. In a high-risk patient population, the pattern of recurrence has been primarily distant with one instance of local tumor recurrence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zagars G K et al. Prognostic factors for patients with localized soft-tissue sarcoma treated with conservation surgery and radiation therapy: an analysis of 1225 patients. Cancer 2003;97: 2530–2543, https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.11365.
Trovik CS et al. Surgical margins, local recurrence and metastasis in soft tissue sarcomas: 559 surgically-treated patients from the Scandinavian Sarcoma Group Register. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:710–716, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(99)00287-7.
Stojadinovic A et al. Analysis of the prognostic significance of microscopic margins in 2084 localized primary adult soft tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg. 2002;235:424–434, https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-200203000-00015.
United States Food and Drug Administration. 510(k) Premarket Notification Database. Accessed on April 29, 2020 via https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm.
Hayes MK. Update on Preoperative Breast Localization. Radiol Clin North Am. 2017;55: 591–603, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcl.2016.12.012.
Flynn N. Merit Medical. Electronic communication. August 31, 2020.
Cox CE et al. A prospective, single arm, multi-site, clinical evaluation of a nonradioactive surgical guidance technology for the location of nonpalpable breast lesions during excision. Ann Surg Oncol 2016;23: 3168–3174, https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5405-y.
Srour M K, Kim S, Amersi F, Giuliano A E, Chung A. Comparison of wire localization, radioactive seed, and Savi Scout(®) radar for management of surgical breast disease. Breast J.2020; 26:406–413, https://doi.org/10.1111/tbj.13499.
Trovik CS et al. Consequences of local recurrence of soft tissue sarcoma: 205 patients from the Scandinavian Sarcoma Group Register. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71:488–495, https://doi.org/10.1080/000164700317381199.
Moureau-Zabotto L et al. Management of soft tissue sarcomas (STS) in first isolated local recurrence: a retrospective study of 83 cases. Radiother Oncol. 2004;73: 313–319, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2004.05.008.
Eilber FC et al. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with locally recurrent extremity soft tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005;12: 228–236, https://doi.org/10.1245/aso.2005.03.045.
Liu C Y et al. Soft tissue sarcoma of extremities: the prognostic significance of adequate surgical margins in primary operation and reoperation after recurrence. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17: 2102–2111, https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-0997-0.
Torres, M. A. et al. Management of locally recurrent soft-tissue sarcoma after prior surgery and radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:1124–1129, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.10.036.
Daigeler A et al. Long-term outcome after local recurrence of soft tissue sarcoma: a retrospective analysis of factors predictive of survival in 135 patients with locally recurrent soft tissue sarcoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;110: 1456–1464, https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.21.
Sugiura H, Tsukushi S, Yoshida M, Nishida Y. What is the success of repeat surgical treatment of a local recurrence after initial wide resection of soft tissue sarcomas? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476 1791–1800, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999.0000000000000158.
Abatzoglou S, Turcotte R E, Adoubali A, Isler M H, Roberge D. Local recurrence after initial multidisciplinary management of soft tissue sarcoma: is there a way out? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468: 3012–3018, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1481-7.
Pouw B et al. Heading toward radioactive seed localization in non-palpable breast cancer surgery? A meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2015;111:185–191, https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.23785.
Jadeja P H et al. Utilization of multiple SAVI SCOUT surgical guidance system reflectors in the same breast: a single-institution feasibility study. Breast J. 2018;24: 531–534, https://doi.org/10.1111/tbj.12979.
Falcon S, Weinfurtner RJ, Mooney B, Niell BL. SAVI SCOUT® localization of breast lesions as a practical alternative to wires: outcomes and suggestions for trouble-shooting. Clin Imaging. 2018;52:280–286, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinimag.2018.07.008.
Zagars G K. et al. Prognostic factors for disease-specific survival after first relapse of soft-tissue sarcoma: analysis of 402 patients with disease relapse after initial conservative surgery and radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;57:739–747, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00714-4.
Acknowledgments
There were no sources of funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Douglas Letson—Stryker Orthopaedics—Consultant.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broman, K.K., Joyce, D., Binitie, O. et al. Intraoperative Localization Using an Implanted Radar Reflector Facilitates Resection of Non-Palpable Trunk and Extremity Sarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol 28, 3366–3374 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09229-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09229-4