Abstract
Introduction
Many clinical manifestations can be related to Tropheryma whipplei infection.
Case report
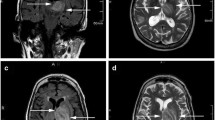
We report a Tropheryma whipplei limbic encephalitis developed as a relapse of classical Whipple’s disease.
Discussion
This case is to the best of our knowledge the first proof of the effective brain–blood barrier crossing of both doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine as demonstrated by direct concentration monitoring on brain biopsy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fenollar F, Puéchal X, Raoult D. Whipple’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:55–66
Mohamed W, Neil E, Kupsky WJ, Juhász C, Mittal S, Santhakumar S. Isolated intracranial Whipple’s disease–report of a rare case and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 2011;308:1–8.
Fenollar F, Nicoli F, Paquet C, Lepidi H, Cozzone P, Antoine J-C, et al. Progressive dementia associated with ataxia or obesity in patients with Tropheryma whipplei encephalitis. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:171.
Blanc F, Ben Abdelghani K, Schramm F, Jaulhac B, Chatelus E, Sordet C, et al. Whipple limbic encephalitis. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1471–3.
Black DF, Aksamit AJ, Morris JM. MR imaging of central nervous system Whipple disease: a 15-year review. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:1493–7.
Fenollar F, Lagier J-C, Raoult D. Tropheryma whipplei and Whipple’s disease. J Infect. 2014;69:103–12.
Lagier J-C, Fenollar F, Lepidi H, Giorgi R, Million M, Raoult D. Treatment of classic Whipple’s disease: from in vitro results to clinical outcome. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69:219–27.
Oyanguren B, Sánchez V, González FJ, de Felipe A, Esteban L, López-Sendón JL, et al. Limbic encephalitis: a clinical-radiological comparison between herpetic and autoimmune etiologies. Eur J Neurol. 2013;20:1566–70.
Scheid R, Lincke T, Voltz R, von Cramon DY, Sabri O. Serial 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis. Arch Neurol. 2004;61:1785–9.
Lagier J-C, Fenollar F, Koric L, Guedj E, Ceccaldi M, Raoult D. Weight loss, dementia and ataxia susceptible to doxycycline: a likely new case report caused by T. whipplei. Rev Médecine Interne Fondée Par Société Natl Francaise Médecine Interne. 2013;34:641–4.
Fenollar F, Perreal C, Raoult D. Tropheryma whipplei natural resistance to trimethoprim and sulphonamides in vitro. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014;43:388–90.
Feurle GE, Moos V, Schneider T, Fenollar F, Raoult D. The combination of chloroquine and minocycline, a therapeutic option in cerebrospinal infection of Whipple’s disease refractory to treatment with ceftriaxone, meropenem and co-trimoxazole. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67:1295–6.
Lagier J-C, Fenollar F, Lepidi H, Raoult D. Evidence of lifetime susceptibility to Tropheryma whipplei in patients with Whipple’s disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:1188–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient for participating. We also thank Pr. Ph. FERNANDEZ for brain 18F-FDG-PET picture, and Dr. Pantxika BELLECAVE, for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. DB and Pr. CC had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data. Study concept and design: DB, IS, DN, CC. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: all authors. Drafting of the manuscript: BB, CC, AD. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: DB, IS, JL, HL, DR, DN, CC. Administrative, technical, or material support: DB, MP, FH. Study supervision: CC.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brönnimann, D., Vareil, MO., Sibon, I. et al. Limbic encephalitis as a relapse of Whipple’s disease with digestive involvement and spondylodiscitis. Infection 47, 637–641 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-018-1173-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-018-1173-x