Abstract
Purpose
Tadalafil seems to ameliorate insulin resistance and glucose homeostasis in humans. We have previously reported that tadalafil targets human skeletal muscle cells with an insulin (I)-like effect. We aim to evaluate in human fetal skeletal muscle cells after tadalafil or I: (i) expression profile of I-regulated genes dedicated to cellular energy control, glycolitic activity or microtubule formation/vesicle transport, as GLUT4, PPARγ, HK2, IRS-1, KIF1C, and KIFAP3; (ii) GLUT4, Flotillin-1, and Caveolin-1 localization, all proteins involved in energy-dependent cell trafficking; (iii) activation of I-targeted paths, as IRS-1, PKB/AKT, mTOR, P70/S6K. Free fatty acids intracellular level was measured. Sildenafil or a cGMP synthetic analog were used for comparison; PDE5 and PDE11 gene expression was evaluated in human fetal skeletal muscle cells.
Methods
RTq-PCR, PCR, western blot, free fatty acid assay commercial kit, and lipid stain non-fluorescent assay were used.
Results
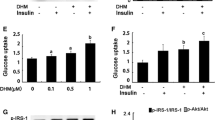
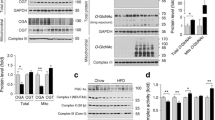
Tadalafil upregulated I-targeted investigated genes with the same temporal pattern as I (GLUT4, PPARγ, and IRS-1 at 3 h; HK2, KIF1C, KIFAP3 at 12 h), re-localized GLUT4 in cell sites positively immune-decorated for Caveolin-1 and Flotillin-1, suggesting the involvement of lipid rafts, induced specific residue phosphorylation of IRS-1/AKT/mTOR complex in association with free fatty acid de novo synthesis. Sildenafil or GMP analog did not affect GLUT4 trafficking or free fatty acid levels.
Conclusion
In human fetal skeletal muscle cells tadalafil likely favors energy storage by modulating lipid homeostasis via IRS-1-mediated mechanisms, involving activation of I-targeted genes and intracellular cascade related to metabolic control. Those data provide some biomolecular evidences explaining, in part, tadalafil-induced favorable control of human metabolism shown by clinical studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.C. Carson, T.F. Lue, Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 96, 257–280 (2005)
J.H. Hong, Y.S. Kwon, I.Y. Kim, Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. Exp. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 13, 183–192 (2017)
M. Dell’Agli, G.V. Galli, E. Dal Cero, F. Belluti, R. Matera, E. Zironi, G. Pagliuca, E. Bosisio, Potent inhibition of human phosphodiesterase-5 by icariin derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 71, 1513–1517 (2008)
A. Basu, R.E. Ryder, New treatment options for erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus. Drugs 64, 2667–2688 (2004)
S.H. Francis, J.D. Corbin, PDE5 inhibitors: targeting erectile dysfunction in diabetics. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 11, 683–688 (2011)
Y.P. Balhara, S. Sarkar, R. Gupta, Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 19, 451–461 (2015)
D. Hatzichristou, M. Gambla, E. Rubio-Aurioles, J. Buvat, G.B. Brock, G. Spera, L. Rose, D. Lording, S. Liang, Efficacy of tadalafil once daily in men with diabetes mellitus and erectile dysfunction. Diabet. Med. 25, 138–46 (2008)
A. Aversa, Systemic and metabolic effects of PDE5-inhibitor drugs. World J. Diabetes 1, 3–7 (2010)
C.E. Ramirez, H. Nian, C. Yu, J.L. Gamboa, J.M. Luther, N.J. Brown, C.A. Shibao, Treatment with Sildenafil Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Prediabetes: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100, 4533–4540 (2015)
L. Fu, F. Li, A. Bruckbauer, Q. Cao, X. Cui, R. Wu, H. Shi, B. Xue, M.B. Zemel, Interaction between leucine and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition in modulating insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 8, 227–239 (2015)
J.E. Ho, P. Arora, G.A. Walford, A. Ghorbani, D.P. Guanaga, B.P. Dhakal, D.I. Nathan, E.S. Buys, J.C. Florez, C. Newton-Cheh, G.D. Lewis, T.J. Wang, Effect of phosphodiesterase inhibition on insulin resistance in obese individuals. J. Am. Heart Assoc. (2014). doi:10.1161/JAHA.114.001001
L. Di Luigi, C. Baldari, P. Sgrò, G.P. Emerenziani, M.C. Gallotta, S. Bianchini, F. Romanelli, F. Pigozzi, A. Lenzi, L. Guidetti, The type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibitor tadalafil influences salivary cortisol, testosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate responses to maximal exercise in healthy men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. (2008). doi:10.1210/jc.2008-0847
L. Di Luigi, C. Baldari, F. Pigozzi, G.P. Emerenziani, M.C. Gallotta, F. Iellamo, E. Ciminelli, P. Sgrò, F. Romanelli, A. Lenzi, L. Guidetti, The long-acting phosphodiesterase inhibitor tadalafil does not influence athletes’ VO2max, aerobic, and anaerobic thresholds in normoxia. Int. J. Sports Med. 29, 110–115 (2008)
H. Duplain, R. Burcelin, C. Sartori, S. Cook, M. Egli, M. Lepori, P. Vollenweider, T. Pedrazzini, P. Nicod, B. Thorens, U. Scherrer, Insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension in mice lacking endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 104, 342–345 (2001)
M. Sheffield-Moore, J.E. Wiktorowicz, K.V. Soman, C.P. Danesi, M.P. Kinsky, E.L. Dillon, K.M. Randolph, S.L. Casperson, D.C. Gore, A.M. Horstman, J.P. Lynch, B.M. Doucet, J.A. Mettler, J.W. Ryder, L.L. Ploutz-Snyder, J.W. Hsu, F. Jahoor, K. Jennings, G.R. White, S.D. McCammon, W.J. Durham, Sildenafil increases muscle protein synthesis and reduces muscle fatigue. Clin. Transl. Sci. 6, 463–468 (2013)
S. Sabatini, P. Sgrò, G. Duranti, R. Ceci, L. Di Luigi, Tadalafil alters energy metabolism in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Acta Biochim. Pol. 58, 237–241 (2011)
C. Crescioli, N. Sturli, M. Sottili, P. Bonini, A. Lenzi, L. Di Luigi, Insulin-like effect of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor tadalafil onto male human skeletal muscle cells. J. Endocrinol. Invest. (2013). doi:10.3275/9034
E. Milani, S. Nikfar, R. Khorasani, M.J. Zamani, M. Abdollahi, Reduction of diabetes-induced oxidative stress by phosphodiesterase inhibitors in rats. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 140, 251–255 (2005)
L. Di Luigi, F. Romanelli, P. Sgrò., A. Lenzi, Andrological aspects of physical exercise and sport medicine. Endocrine 42, 278–284 (2012)
L. Di Luigi, Supplements and the endocrine system in athletes. Clin. Sports Med. 27, 131–151 (2008)
C. Baldari, L. Di Luigi, G.P. Emerenziani, M.C. Gallotta, P. Sgrò, L. Guidetti, Is explosive performance influenced by androgen concentrations in young male soccer players? Br. J. Sports Med. 43, 191–194 (2009)
R.A. De Fronzo, E. Jacot, E. Jequier, E. Maeder, J. Wahren, J.P. Felber, The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes 30, 1000–1007 (1981)
C. Crescioli, M. Sottili, P. Bonini, L. Cosmi, P. Chiarugi, P. Romagnani, G.B. Vannelli, M. Colletti, A.M. Isidori, M. Serio, A. Lenzi, L. Di Luigi, Inflammatory response in human skeletal muscle cells: CXCL10 as a potential therapeutic target. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 91, 139–149 (2012)
C. Antinozzi, C. Corinaldesi, C. Giordano, A. Pisano, B. Cerbelli, S. Migliaccio, L. Di Luigi, K. Stefanantoni, G.B. Vannelli, S. Minisola, G. Valesini, V. Riccieri, A. Lenzi, C. Crescioli, Potential role for the VDR agonist elocalcitol in metabolic control: Evidences in human skeletal muscle cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 167, 169–181 (2017)
Z.W. Yu, J. Burén, S. Enerbäck, E. Nilsson, L. Samuelsson, J.W. Eriksson, Insulin can enhance GLUT4 gene expression in 3T3-F442A cells and this effect is mimicked by vanadate but counteracted by cAMP and high glucose--potential implications for insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1535, 174–185 (2001)
J. Rieusset, F. Andreelli, D. Auboeuf, M. Roques, P. Vallier, J.P. Riou, J. Auwerx, M. Laville, H. Vidal, Insulin acutely regulates the expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in human adipocytes. Diabetes 48, 699–705 (1999)
H. Osawa, C. Sutherland, R.B. Robey, R.L. Printz, D.K. Granner, Analysis of the signaling pathway involved in the regulation of hexokinase II gene transcription by insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 16690–16694 (1996)
S. Rome, K. Clément, R. Rabasa-Lhoret, E. Loizon, C. Poitou, G.S. Barsh, J.P. Riou, M. Laville, H. Vidal, Microarray profiling of human skeletal muscle reveals that insulin regulates approximately 800 genes during a hyperinsulinemic clamp. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 18063–18068 (2003)
K.A. Cho, P.B. Kang, PLIN2 inhibits insulin-induced glucose uptake in myoblasts through the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. J. Mol. Med. 36, 839–844 (2015)
P. Gallina, M. Paganini, L. Lombardini, R. Saccardi, M. Marini, M.T. De Cristofaro, P. Pinzani, F. Salvianti, C. Crescioli, A. Di Rita., S. Bucciantini, C. Mechi, E. Sarchielli, M. Moretti, S. Piacentini, G. Gritti, A. Bosi, S. Sorbi, G. Orlandini, G.B. Vannelli, N. Di Lorenzo, Development of human striatal anlagen after transplantation in a patient with Huntington’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 213, 241–244 (2008)
A. Aversa, M. Caprio, A. Antelmi, A. Armani, M. Brama, E.A. Greco, D. Francomano, M. Calanchini, G. Spera, L. Di Luigi, G.M. Rosano, A. Lenzi, S. Migliaccio, A. Fabbri, Exposure to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors stimulates aromatase expression in human adipocytes in vitro. J. Sex. Med. 8, 696–704 (2011)
S. Marchiani, L. Bonaccorsi, P. Ferruzzi, C. Crescioli, M. Muratori, L. Adorini, G. Forti, M. Maggi, E. Baldi, The vitamin D analogue BXL-628 inhibits growth factor-stimulated proliferation and invasion of DU145 prostate cancer cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 132, 408–416 (2006)
G.L. Gravina, F. Marampon, P. Muzi, A. Mancini, M. Piccolella, P. Negri-Cesi, M. Motta, A. Lenzi, E. Di Cesare, V. Tombolini, E.A. Jannini, C. Festuccia, PXD101 potentiates hormonal therapy and prevents the onset of castration-resistant phenotype modulating androgen receptor, HSP90, and CRM1 in preclinical models of prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. (2013). doi:10.1530/ERC-12-0240
L. Di Luigi, M. Sottili, C. Antinozzi, G.B. Vannelli, F. Romanelli, V. Riccieri, G. Valesini, A. Lenzi, C. Crescioli, The vitamin D receptor agonist BXL-01-0029 as a potential new pharmacological tool for the treatment of inflammatory myopathies. PLoS One. (2013). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077745
E.J. Henriksen, B.B. Dokken, Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Curr Drug Targets 7, 1435–1441 (2006)
S. Uckert, P. Hedlund, K.E. Andersson, M.C. Truss, U. Jonas, C.G. Stief, Update on phosphodiesterase (PDE) isoenzymes as pharmacologic targets in urology: present and future. Eur Urol. 50, 1194–1207 (2006)
J.E. Ayala, D.P. Bracy, B.M. Julien, J.N. Rottman, P.T. Fueger, D.H. Wasserman, Chronic treatment with sildenafil improves energy balance and insulin action in high fat-fed conscious mice. Diabetes 56, 1025–1033 (2007)
L. Fu, F. Li, A. Bruckbauer, Q. Cao, X. Cui, R. Wu, H. Shi, B. Xue, M.B. Zemel, Interaction between leucine and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition in modulating insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. (2015). doi:10.2147/DMSO.S82338
P.A. Jansson, G. Murdolo, L. Sjögren, B. Nyström, M. Sjöstrand, L. Strindberg, P. Lönnroth, Tadalafil increases muscle capillary recruitment and forearm glucose uptake in women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 53, 2205–2208 (2010)
L. Sjögren, J. Olausson, L. Strindberg, R. Mobini, P. Fogelstrand, L. Mattsson Hultén, P.A. Jansson, Postprandial effects of the phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor tadalafil in people with well-controlled Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Diabet. Med. 33, 1299–1301 (2016)
G. Murdolo, M. Sjöstrand, L. Strindberg, P. Lönnroth, P.A. Jansson, The selective phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor tadalafil induces microvascular and metabolic effects in type 2 diabetic postmenopausal females. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98, 245–254 (2013)
C. McMahon, Efficacy and safety of daily tadalafil in men with erectile dysfunction previously unresponsive to on-demand tadalafil. J. Sex Med. 1, 292–300 (2004)
B.E. Sansbury, B.G. Hill, Regulation of obesity and insulin resistance by nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 73, 383–399 (2014)
U. Förstermann, T. Münzel, Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace. Circulation 113, 1708–1714 (2006)
J.M. Richey, The vascular endothelium, a benign restrictive barrier? NO! Role of nitric oxide in regulating insulin action. Diabetes. (2013). doi:10.2337/db13-1395
M. Kanzaki, J.E. Pessin, Insulin signaling: GLUT4 vesicles exit via the exocyst. Curr. Biol. 15, 574–576 (2003)
J.B. Helms, C. Zurzolo, Lipids as targeting signals: lipid rafts and intracellular trafficking. Traffic 5, 247–54 (2004)
L.H. Chamberlain, G.W. Gould, The vesicle- and target-SNARE proteins that mediate Glut4 vesicle fusion are localized in detergent-insoluble lipid rafts present on distinct intracellular membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 49750–49754 (2002)
A. Ros-Baro, C. Lopez-Iglesias, S. Peiro, D. Bellido, M. Palacin, A. Zorzano, M. Camps, Lipid rafts are required for GLUT4 internalization in adipose cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 98, 12050–12055 (2001)
K. Fecchi, D. Volonte, M.P. Hezel, K. Schmeck, F. Galbiati, Spatial and temporal regulation of GLUT4 translocation by flotillin-1 and caveolin-3 in skeletal muscle cells. FASEB J. 20, 705–707 (2006)
E. González-Muñoz, C. López-Iglesias, M. Calvo, M. Palacín, A. Zorzano, M. Camps, Caveolin-1 loss of function accelerates glucose transporter 4 and insulin receptor degradation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrinology 150, 3493–3502 (2009)
Y. Hoon Son, S.J. Lee, K.B. Lee, J.H. Lee, E.M. Jeong, S.C. Chung, S.C. Park, I.G. Kim, Dexamethasone downregulates caveolin-1 causing muscle atrophy via inhibited insulin signaling. J. Endocrinol. 225, 27–37 (2005)
Y.S. Oh, L.Y. Khil, K.A. Cho, S.J. Ryu, M.K. Ha, G.J. Cheon, T.S. Lee, J.W. Yoon, H.S. Jun, S.C. Park, A potential role for skeletal muscle caveolin-1 as an insulin sensitivity modulator in ageing-dependent non-obese type 2 diabetes: studies in a new mouse model. Diabetologia 51, 1025–1034 (2008)
M. Laplante, D.M. Sabatini, mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149, 274–293 (2012)
D.A. Altomare, A.R. Khaled, Homeostasis and the importance for a balance between AKT/mTOR activity and intracellular signaling. Curr. Med. Chem. 9, 3748–3762 (2012)
N. Takei, H. Nawa, mTOR signaling and its roles in normal and abnormal brain development. Front. Mol. Neurosci. (2014). doi:10.3389/fnmol.2014.00028
M. Gao, J. Liang, Y. Lu, H. Guo, P. German, S. Bai, E. Jonasch, X. Yang, G.B. Mills, Z. Ding, Site-specific activation of AKT protects cells from death induced by glucose deprivation. Oncogene. 33, 745–755 (2014)
S.F. Moore, R.W. Hunter, I. Hers, mTORC2 protein complex-mediated Akt (Protein Kinase B) Serine 473 Phosphorylation is not required for Akt1 activity in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 24553–24560 (2011)
L. Vadlakonda, A. Dash, M. Pasupuleti, K. Anil Kumar, P. Reddanna, The Paradox of Akt-mTOR Interactions. Front. Oncol. (2013). doi:10.3389/fonc.2013.00165
C.A. Moody, R.S. Scott, N. Amirghahari, C.O. Nathan, L.S. Young, C.W. Dawson, J.W. Sixbey, Modulation of the cell growth regulator mTOR by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A. J. Virol. 79, 5499–5506 (2005)
C. Gao, C. Hölscher, Y. Liu, L. Li, GSK3: a key target for the development of novel treatments for type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer disease. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 1–11 (2011)
M. Laplante, D.M. Sabatini, mTOR signaling at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. (2009). doi:10.1242/jcs.051011
T. Porstmann, C.R. Santos, B. Griffiths, M. Cully, M. Wu, S. Leevers, J.R. Griffiths, Y.L. Chung, A. Schulze, SREBP activity is regulated by mTORC1 and contributes to Akt-dependent cell growth. Cell Metab. 8, 224–236 (2008)
J.E. Kim, J. Chen, Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activity by mammalian target of rapamycin and amino acids in adipogenesis. Diabetes 53, 2748–2756 (2004)
C. Fernández-Hernando, K.J. Moore, MicroRNA modulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31, 2378–2382 (2011)
M.A. Bouhlel, B. Staels, G. Chinetti-Gbaguidi, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors--from active regulators of macrophage biology to pharmacological targets in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. J. Intern. Med. 263, 28–42 (2008)
L. Luo, M. Liu, Adipose tissue in control of metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 231, R77–R99 (2016)
M. Coelho, T. Oliveira, R. Fernandes, Biochemistry of adipose tissue: an endocrine organ. Arch. Med. Sci. 9, 191–200 (2013)
L.J. van Loon, B.H. Goodpaster, Increased intramuscular lipid storage in the insulin-resistant and endurance-trained state. Pflugers Arch. 451, 606–616 (2006)
B.H. Goodpaster, J. He, S. Watkins, D.E. Kelley, Skeletal muscle lipid content and insulin resistance: evidence for a paradox in endurance-trained athletes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 5755–5761 (2001)
A.P. Russell, Lipotoxicity: the obese and endurance-trained paradox. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 28, S66–S71 (2004)
Z. Guo, L. Zhou, M.D. Jensen, Acute hyperinsulinemia inhibits intramyocellular triglyceride synthesis in high-fat-fed obese rats. J. Lipid Res. 47, 2640–2646 (2006)
Y. Li, S. Xu, X. Zhang, Z. Yi, S. Cichello, Skeletal intramyocellular lipid metabolism and insulin resistance. Biophys. Rep. 1, 90–98 (2015)
M.E. Young, B. Leighton, Fuel oxidation in skeletal muscle is increased by nitric oxide/cGMP--evidence for involvement of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 424, 79–83 (1998)
M.E. Young, G.K. Radda, B. Leighton, Nitric oxide stimulates glucose transport and metabolism in rat skeletal muscle in vitro. Biochem. J. 322, 223–228 (1997)
Y. Higaki, M.F. Hirshman, N. Fujii, L.J. Goodyear, Nitric oxide increases glucose uptake through a mechanism that is distinct from the insulin and contraction pathways in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes 50, 241–247 (2001)
K. Loughney, J. Taylor, V.A. Florio, 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 11A: localization in human tissues. Int. J. Impot. Res. 17, 320–325 (2005)
G. Kakik, N.S. Tuzun, S. Durdagi, Investigation of PDE5/PDE6 and PDE5/PDE11 selective potent tadalafil-like PDE5 inhibitors using combination of molecular modeling approaches, molecular fingerprint-based virtual screening protocols and structure-based pharmacophore development. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 32, 311–330 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This report was supported by ELI Lilly ICOS Corporation, Indianapolis, USA.
Funding
This study was funded by ELI LILLY (Ex NCR H6D-IT-V015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Crescioli C declares that she has received research grants from Company ELI LILLY. All the other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
F. Marampon and C. Antinozzi contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marampon, F., Antinozzi, C., Corinaldesi, C. et al. The phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor tadalafil regulates lipidic homeostasis in human skeletal muscle cell metabolism. Endocrine 59, 602–613 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1378-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1378-2