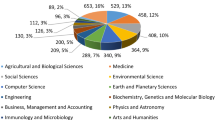
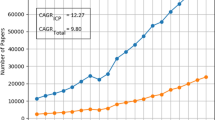
Abstract
Scientometric studies have, by and large, focused on the features of the hard sciences rather than the soft sciences. Prior research has been highly centered around natural science disciplines and not many studies have dealt with the social sciences. This applies to Africa as well. However, attempts to investigate the features and tendencies in the social sciences are gradually emerging. This is the first paper to explore the social sciences in South Africa, examining the interrelationships between the types of collaboration and the impact of research publications as measured in the count of citations. Extracting Web of Science data from its Social Science Citation Index (from 1956 to present) for sampled years between 1970 and 2015 (n = 4991), the analysis explains citations in terms of the type of collaboration, international partners and subject areas. The highlights of this analysis are that the social sciences in South Africa have certain distinguishing characteristics that determine the production and impact on knowledge.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
http://ipsciencehelp.thomsonreuters.com/incitesLive/globalComparisonsGroup/globalComparisons/sbAreaSchemesGroup/oecd.html. In the WoS dataset there were some publications that were not socialscience subjects. These were removed before the analysis was done.
The advanced search option of the Web of Science, Core Collection (under which Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) 1956–present was selected) was used. Publications (all languages, articles and reviews) of South African authors (CU = South Africa) were searched. The time span chosen was all the sampled years of 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2015, which was done individually for each year.
The total percentage of internal-institutional and external-institutional collaboration is not 100% as they are not exclusive categories of domestic collaboration. In other words, a publication might have both types of collaboration.
References
Barrantes, B. S. L., Bote, V. P. G., Rodríguez, Z. C., & Anegón, F. D. M. (2012). Citation flows in the zones of influence of scientific collaborations. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 63(3), 481–489.
Basson, I., & Prozesky, H. E. (2015). A review of methodological trends in South African sociology, 1990–2009. South African Review of Sociology, 46(3), 4–27.
Bornmann, L. (2016). Is collaboration among scientists related to the citation impact of papers because their quality increases with collaboration? An analysis based on data from F1000Prime and normalized citation scores. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology. doi:10.1002/asi.23728.
Bornmann, L., & Daniel, H.-D. (2008). What do citation counts measure? A review of studies on citing behavior. Journal of Documentation, 61(1), 45–80.
CREST (Centre for Research on Evaluation, Science and Technology). (2014). Mapping social sciences research in South Africa. Cape Town: CREST.
Didegah, F., & Thelwall, M. (2013). Which factors help authors produce the highest impact research? Collaboration, journal and document properties. Journal of informetrics, 7, 861–873.
Engels, T. C. E., Ossenblok, T. L. B., & Spruyt, E. H. J. (2012). Changing publication patterns in the social sciences and humanities, 2000–2009. Scientometrics, 93, 373–390.
Falagas, M. E., Zarkali, A., Karageorgopoulos, D. E., Bardakas, V., & Mavros, M. N. (2013). The impact of article length on the number of future citations: A bibliometric analysis of general medicine journals. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049476.
Frenken, K., Ponds, R., & Oort, F. V. (2010). The citation impact of research collaboration in science-based industries: A spatial-institutional analysis. Papers in Regional Science, 89(2), 351–371.
Gazni, A., & Didegah, F. (2011). Investigating different types of research collaboration and citation impact: A case study of Harvard University’s Publications. Scientometrics, 81, 251–265.
Gazni, A., Lariviére, V., & Didegah, F. (2016). The effect of collaborators on institutions’ scientific impact. Scientometrics. doi:10.1007/s11192-016-2101-4.
Gazni, A., & Thelwall, M. (2014). The long-term influence of collaboration on citation patterns. Research Evaluation, 23, 261–271.
Gómez, I., Fernández, M. T., & Sebastián, J. (1999). Analysis of the structure of international scientific cooperation networks through bibliometric indicators. Scientometrics, 44(3), 441–457.
Ingwersen, P. (2000). The international visibility and citation impact of Scandinavian research articles in selected social science fields: The decay of a myth. Scientometrics, 49(1), 39–61.
Iribarren-Maestro, I., Lascurain-Sánchez, M. L., & Sanz-Casado, E. (2009). The use of bibliometric techniques in evaluating social sciences and humanities. In F. Åström, R. Danell, B. Larsen & J. W. Schneider (Eds.), Celebrating scholarly communication studies a festschrift for Olle Persson at his 60th birthday (pp. 25–38). International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics.
Kahn, M. (2011). A bibliometric analysis of South Africa’s scientific outputs: Some trends and implications. South African Journal of Science. doi:10.4102/sajs.vl4107il/4102.4406.
Khor, K. A., & Yu, L.-G. (2016). Influence of international co-authorship on the research citation impact of young universities. Scientometrics, 107, 1095–1110.
Krampen, G., Weiland, P., & Wiesenhütter, J. (2015). Citation success of different publication types: A case study on all references in psychology publications from the German-speaking countries (D–A–CH–L–L) in 2009, 2010, and 2011. Scientometrics, 104, 827–840.
Levitt, J. M., & Thelwall, M. (2010). Does the higher citation of collaborative research differ from region to region? A case study of Economics. Scientometrics, 85(1), 171–183.
Low, W. Y., Ng, K. H., Kabir, M. A., Koh, A. P., & Sinnasamy, J. (2014). Trend and impact of international collaboration in clinical medicine papers published in Malaysia. Scientometrics, 98, 1521–1533.
Mouton, J. (2011). The humanities and social sciences in SA: Crisis or cause for concern? South African Journal of Science, 107(11/12), 1–4.
Narin, F., Stevens, K., & Whitlow, E. S. (1991). Scientific co-operation in Europe and the citation of multinationally authored papers. Scientometrics, 21(3), 313–323.
Nederhof, A. J. (2006). Bibliometric monitoring of research performance in the social sciences and the humanities: A review. Scientometrics, 66(1), 81–100.
Olmos-Peñuela, J., Castro-Martínez, E., & D’EsteI, P. (2014). Knowledge transfer activities in social sciences and humanities: Explaining the interactions of research groups with non-academic agents. Research Policy, 43, 696–706.
Onodera, N., & Yoshikane, F. (2015). Factors affecting citation rates of research articles. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 66(4), 739–764.
Ossenblok, T., Engels, T., & Sivertsen, G. (2012). The representation of the social sciences and humanities in the Web of Science: A comparison of publication patterns and incentive structures in Flanders and Norway (2005–9). Research Evaluation, 21(4), 280–290.
Peng, T.-Q., & Zhu, J. J. H. (2012). Where you publish matters most: A multilevel analysis of factors affecting citations of Internet studies. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 63(9), 1789–1803.
Persson, O. (2010). Are highly cited papers more international? Scientometrics, 83, 397–401.
Pouris, A. (2006). A bibliometric assessment of South African research publications included in the internationally indexed database of Thomson ISI Report on a Strategic Approach to Research Publishing in South Africa in South Africa (pp. 9–29). Pretoria: Academy of Science of South Africa.
Puuska, H.-M., Muhonen, R., & Leino, Y. (2014). International and domestic co-publishing and their citation impact in different disciplines. Scientometrics, 98, 823–839.
Sin, S.-C. J. (2011). International coauthorship and citation impact: A bibliometric study of six LIS journals, 1980–2008. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 62(9), 1770–1783.
Sivertsen, G., & Larsen, B. (2012). Comprehensive bibliographic coverage of the social sciences and humanities in a citation index: An empirical analysis of the potential. Scientometrics, 91, 567–575.
Smith, M. J., Weinberger, C., Bruna, E. M., & Allesina, S. (2014). The scientific impact of nations: Journal placement and citation performance. PLoS ONE, 9(10), e109195. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109195.
Sooryamoorthy, R. (2009a). Do types of collaboration change citation? Collaboration and citation patterns of South African science publications. Scientometrics, 81(1), 171–193.
Sooryamoorthy, R. (2009b). Collaboration and publication: How collaborative are scientists in South Africa? Scientometrics, 80(2), 419–439.
Sooryamoorthy, R. (2015a). Transforming science in South Africa: Development, collaboration and productivity. Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan.
Sooryamoorthy, R. (2015b). Sociological research in South Africa: Post-apartheid trends. International Sociology Reviews, 30(2), 119–133.
Sooryamoorthy, R. (2016). Sociology in South Africa: Colonial, apartheid and democratic forms. Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan.
Thompson, J. W. (2002). The death of the scholarly monograph in the humanities? Citation patterns in literary scholarship. Libri, 52, 121–136.
Tsai, C.-C., Corley, E. A., & Bozeman, B. (2016). Collaboration experiences across scientific disciplines and cohorts. Scientometrics. doi:10.1007/s11192-016-1997z.
van Leeuwen, T. (2006). The application of bibliometric analyses in the evaluation of social science research. Who benefits from it, and why it is still feasible. Scientometrics, 66(1), 133–154.
Wallace, M. L., Larivière, V., & Gingras, Y. (2012). A small world of citations? The influence of collaboration networks on citation practices. PLoS ONE, 7(3), e33339.
Xia, X., Wang, Z., Wu, Y., Ruan, L., & Wang, L. (2014). Country of authorship and collaboration affect citations of articles by South and East Asian authors in agronomy journals: A case study of China, Japan, and India. Serials Review, 40, 118–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sooryamoorthy, R. Do types of collaboration change citation? A scientometric analysis of social science publications in South Africa. Scientometrics 111, 379–400 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2265-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2265-6