Abstract
Purpose
Phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitor administration in diabetic men with erectile dysfunction (ED) is associated with reduced waist circumference. We evaluated potential effects of daily tadalafil administration on body composition and investigated its possible mechanism(s) of action in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells in vitro.
Methods
Forty-three men on stable caloric intake (mean age 48.5 ± 7; BMI 25.5 ± 0.9 kg/m2) complaining mild ED and/or low urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) were randomly assigned to receive tadalafil (TAD) 5 mg/daily (once-a-day=OAD-TAD; n = 23) or 20 mg on-demand (on-demand=OD-TAD; n = 20) for 2 months. Primary outcomes were variations of body composition measured by Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; secondary outcomes were ED/LUTS questionnaire scores along with hormone (testosterone, estradiol, insulin) and endothelial function (Endopat2000) variations.
Results
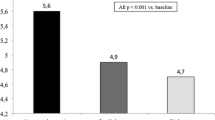
OAD-TAD increased abdominal lean mass (p < 0.01) that returned to baseline after 2 months withdrawal. LUTS scores improved (p<0.01) in OD-TAD while ED scores improved (p < 0.01) in both groups. We found significant improvements in endothelial function (p < 0.05) that directly correlated with serum insulin (p < 0.01; r = 0.3641) and inversely correlated with estradiol levels (p < 0.01; r = 0.3655) even when corrected for potential confounders. Exposure of C2C12 cells upon increasing tadalafil concentrations (10−7 to 10−6 M) increased total androgen receptor mRNA and protein expression as well as myogenin protein expression after 24 and 72 h (2.8 ± 0.4-fold and 1.4 ± 0.02-fold vs. control, respectively, p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Daily tadalafil improved lean mass content in non-obese men probably via enhanced insulin secretion, estradiol reduction, and improvement of endothelial function in vivo. The in vitro increased myogenin and androgen receptor protein expression in skeletal muscle cells suggests a translational action of phosphodiesterase type-5 on this receptor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.H. Soderling, J.A. Beavo, Regulation of cAMP and cGMP signalling: new phosphodiesterases and new functions. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 12, 174–179 (2000)
N.T. Dickinson, E.K. Jang, R.J. Haslam, Activation of cGMP-stimulated phosphodiesterase by nitroprusside limits cAMP accumulation in human platelets: effects on platelet aggregation. Biochem. J. 323, 371–377 (1997)
K. Omori, J. Kotera, Overview of PDEs and their regulation. Circ. Res. 100, 309–327 (2007)
M.E. Young, B. Leighton, Evidence for altered sensitivity of the nitric oxide/cGMP signalling cascade in insulin-resistant skeletal muscle. Biochem. J. 329, 73–79 (1998)
S. Collins, T.L. Martin, R.S.J. Surwit, J. Robidoux, Genetic vulnerability to diet-induced obesity in the C57BL/6J mouse: physiological and molecular characteristics. Physiol. Behav. 81, 243–248 (2004)
A. Aversa, E. Greco, R. Bruzziches, M. Pili, G. Rosano, G. Spera, Relationship between chronic tadalafil administration and improvement of endothelial function in men with erectile dysfunction: a pilot study. Int. J. Impot. Res. 19, 200–207 (2007)
D. Santi, E. Giannetta, A.M. Isidori, C. Vitale, A. Aversa, M. Simoni, Effects of chronic use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on endothelial markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 172, R103–114 (2015)
A. Aversa, M. Caprio, A. Antelmi et al. Exposure to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors stimulates aromatase expression in human adipocytes in vitro. J. Sex. Med. 8, 696–704 (2011)
A. Aversa, S. Fittipaldi, V.M. Bimonte et al. Tadalafil modulates aromatase activity and androgen receptor expression in a human osteoblastic cell in vitro model. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 39, 199–205 (2016)
E. Maneschi, I. Cellai, A. Aversa et al. Tadalafil reduces visceral adipose tissue accumulation by promoting preadipocytes differentiation towards a metabolically healthy phenotype: studies in rabbits. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 424, 50–70 (2016)
D. Fiore, D. Gianfrilli, E. Giannetta et al. PDE5 inhibition ameliorates visceral adiposity targeting the miR-22/SIRT1 pathway: evidence from the CECSID Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 101, 1525–1534 (2016)
K.D. Lee, Androgen receptor enhances myogenin expression and accelerates differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 294, 408–413 (2002)
S. Sabatini, P. Sgrò, G. Duranti, R. Ceci, L. Di Luigi, Tadalafil alters energy metabolism in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Acta. Biochim. Pol. 58, 237–242 (2011)
F. Wannenes, M. Caprio, L. Gatta, A. Fabbri, S. Bonini, C. Moretti, Androgen receptor expression during C2C12 skeletal muscle cell line differentiation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 24(292), 11–19 (2008)
M.P. Rothney, Y. Xia, W.K. Wacker et al. Precision of a new tool to measure visceral adipose tissue (VAT) using dualenergy X-Ray absorptiometry (DXA). Obesity (Silver Spring). 21, E134–E136 (2013)
A. Aversa, D. Francomano, R. Bruzziches et al. The application of digital pulse amplitude tonometry to the diagnostic investigation of endothelial dysfunction in men with erectile dysfunction. Andrologia 43, 9–15 (2011)
A. Aversa, C. Letizia, D. Francomano, R. Bruzziches, M. Natali, A. Lenzi, A spontaneous, double-blind, double-dummy cross-over study on the effects of daily vardenafil on arterial stiffness in patients with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiol. 160, 187–191 (2012)
G. Antonini, A. Clemenzi, E. Bucci et al. Hypogonadism in DM1 and its relationship to erectile dysfunction. J. Neurol. 258, 1247–1253 (2011)
C. Crescioli, N. Sturli, M. Sottili, P. Bonini, A. Lenzi, L. Di Luigi, Insulin-like effect of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor tadalafil onto male human skeletal muscle cells. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 36, 1020–6 (2013)
A. Morelli, S. Filippi, R. Mancina et al. Androgens regulate phosphodiesterase type 5 expression and functional activity in corpora cavernosa. Endocrinology. 145, 2253–2263 (2004)
S. Engeli, A.L. Birkenfeld, P.M. Badin, V. Bourlier, K. Louche, N. Viguerie et al. Natriuretic peptides enhance the oxidative capacity of human skeletal muscle. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 4675–46759 (2012)
H. Duplain, R. Burcelin, C. Sartori et al. Insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension in mice lacking endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation. 104, 342–345 (2001)
M.E. Young, B. Leighton, Evidence for altered sensitivity of the nitric oxide/cGMP signalling cascade in insulin-resistant skeletal muscle. Biochem. J. 329(Pt 1), 73–79 (1998)
J.E. Ayala, D.P. Bracy, B.M. Julien et al. Chronic treatment with sildenafil improves energy balance and insulin action in high fat-fed conscious mice. Diabetes. 56, 1025–1033 (2007)
F.N. Salloum, A. Abbate, A. Das et al. Sildenafil (Viagra) attenuates ischemic cardiomyopathy and improves left ventricular function in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 294, H1398–H1406 (2008)
N.G. Pérez, M.R. Piaggio, I.L. Ennis et al. Phosphodiesterase 5A inhibition induces Na+/H + exchanger blockade and protection against myocardial infarction. Hypertension 49, 1095–1103 (2007)
C.E. Ramirez, H. Nian, C. Yu, J.L. Gamboa, J.M. Luther, N.J. Brown, C.A. Shibao, Treatment with Sildenafil Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Prediabetes: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100, 4533–4540 (2015)
K.D. Hill, A.W. Eckhauser, A. Marney, N.J. Brown, Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition improves beta-cell function in metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 32, 857–859 (2009)
P.A. Jansson, G. Murdolo, L. Sjögren, B. Nyström, M. Sjöstrand, L. Strindberg et al. Tadalafil increases muscle capillary recruitment and forearm glucose uptake in women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 53, 2205–2208 (2010)
J. Tooke, The association between insulin resistance and endotheliopathy. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 1(Suppl. 1), S17–S22 (1999)
I.C. Yu, H.Y. Lin, J.D. Sparks, S. Yeh, C. Chang, Androgen receptor roles in insulin resistance and obesity in males: the linkage of androgen-deprivation therapy to metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 63, 3180–3188 (2014)
S.J. Tapscott, The circuitry of a master switch: Myo-d and the regulation of skeletal muscle gene transcription. Development 132, 2685–2695 (2005)
V. Andrés, K. Walsh, Myogenin expression, cell cycle withdrawal, and phenotypic differentiation are temporally separable events that precede cell fusion upon myogenesis. J. Cell. Biol. Feb. 132, 657–666 (1996)
J. Henningsen, K.T. Rigbolt, B. Blagoev, B.K. Pedersen, I. Kratchmarova, Dynamics of the skeletal muscle secretome during myoblast differentiation. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 9, 2482–2496 (2010)
E.A. Greco, M. Pili, R. Bruzziches, G. Corona, G. Spera, A. Aversa, Testosterone: estradiol ratio changes associated with long-term tadalafil administration: a pilot study. J. Sex. Med. 3, 716–722 (2006)
Y. Kanno, R. Ota, K. Someya, T. Kusakabe, K. Kato, Y. Inouye, Selective androgen receptor modulator, YK11, regulates myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts by follistatin expression. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 36, 1460–1465 (2013)
L. Di Luigi, C. Baldari, P. Sgrò et al. The type 5 phosphodiesterase’s inhibitor tadalafil influences salivary cortisol, testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate response to maximal exercise in healthy man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 3510–3514 (2008)
L. Di Luigi, C. Baldari, F. Pigozzi et al. The long-acting phosphodiesterase inhibitor tadalafil does not influence athletes’ VO2max, aerobic, and anaerobic thresholds in normoxia. Int. J. Sports Med. 29, 110–115 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Andrea D’Anselmo for revising the English language.
Funding
This study was funded by MIUR Grants (grant number 2015XCR88M_008 to Prof. Antonio Aversa and 052013 to Prof. Silvia Migliaccio) and Ministry of Health Grant (grant number 00829 to Prof. Andrea Lenzi).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards (NCT Identifier: NCT02554045).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aversa, A., Fittipaldi, S., Francomano, D. et al. Tadalafil improves lean mass and endothelial function in nonobese men with mild ED/LUTS: in vivo and in vitro characterization. Endocrine 56, 639–648 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1208-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1208-y