Abstract
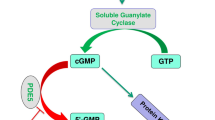
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) represents a worldwide health problem. Traditionally, the nephroprotective treatment for CKD aims to slow progression to end-stage renal disease and includes dietary protein restriction, correction of metabolic acidosis, and renin–angiotensin system blockers. However, current standard therapeutic options may not be enough for preventing CKD progression in a subset of patients making necessary to develop novel therapeutic options to further slow renal function loss. Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors represent a class of drugs traditionally used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension. However, recent evidence suggests that PDE5 inhibitors may have additional therapeutic effects, such as cardioprotection and cerebrovascular protection. In the current review, we summarize PDE5 inhibitors’ utility in disease states and clinical conditions related to kidney disease such as systemic hypertension and acute and chronic kidney injury and discuss the mechanisms explaining possible kidney protective roles of PDE5 inhibitors. A recently completed phase 2 trials demonstrated that the long-acting PDE5 inhibitor PF-00489791 decreased albuminuria in patients with overt diabetic nephropathy when added on top of renin–angiotensin system blockade.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bello AK, Levin A, Manns BJ et al (2015) Effective CKD care in European countries: challenges and opportunities for health policy. Am J Kidney Dis 65:15–25
Mortality GBD (2015) Causes of death C: global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 385:117–171
Klahr S, Schreiner G, Ichikawa I (1988) The progression of renal disease. N Engl J Med 318:1657–1666
Bae EH, Kim IJ, Joo SY et al (2012) Renoprotective effects of sildenafil in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Kidney Blood Press Res 36:248–257
Stefoni S, Cianciolo G, Baraldi O et al (2014) Emerging drugs for chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 19:183–199
Drawz PE, Rosenberg ME (2011) Slowing progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 3(372–376):2013
Pippias M, Stel VS, Abad Diez JM et al (2015) Renal replacement therapy in Europe: a summary of the 2012 ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report. Clin Kidney J 8:248–261
Gonzalez-Espinoza L, Ortiz A (2015) 2012 ERA-EDTA Registry Annual Report: cautious optimism on outcomes, concern about persistent inequalities and data black-outs. Clin Kidney J 8:243–247
Gordon J, Kopp JB (2011) Off the beaten renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system pathway: new perspectives on antiproteinuric therapy. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 18:300–311
Fernandez-Fernandez B, Ortiz A, Gomez-Guerrero C et al (2014) Therapeutic approaches to diabetic nephropathy–beyond the RAS. Nat Rev Nephrol 10:325–346
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Mora-Fernandez C, Muros de Fuentes M et al (2015) Effect of pentoxifylline on renal function and urinary albumin excretion in patients with diabetic kidney disease: the PREDIAN trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:220–229
Kuno Y, Iyoda M, Shibata T et al (2011) Sildenafil, a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor, attenuates diabetic nephropathy in non-insulin-dependent Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Br J Pharmacol 162:1389–1400
Chen HH, Huntley BK, Schirger JA et al (2006) Maximizing the renal cyclic 3′-5′-guanosine monophosphate system with type V phosphodiesterase inhibition and exogenous natriuretic peptide: a novel strategy to improve renal function in experimental overt heart failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2742–2747
Sohotnik R, Nativ O, Abbasi A et al (2013) Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition attenuates early renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury: assessment by quantitative measurement of urinary NGAL and KIM-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304:F1099–F1104
Jackson G, Benjamin N, Jackson N et al (1999) Effects of sildenafil citrate on human hemodynamics. Am J Cardiol 83:13C–20C
Mahmud A, Hennessy M, Feely J (2001) Effect of sildenafil on blood pressure and arterial wave reflection in treated hypertensive men. J Hum Hypertens 15:707–713
Kloner RA, Mitchell M, Emmick JT (2003) Cardiovascular effects of tadalafil in patients on common antihypertensive therapies. Am J Cardiol 92:47M–57M
Oliver JJ, Melville VP, Webb DJ (2006) Effect of regular phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition in hypertension. Hypertension 48:622–627
Pomara G, Morelli G, Pomara S et al (2004) Cardiovascular parameter changes in patients with erectile dysfunction using pde-5 inhibitors: a study with sildenafil and vardenafil. J Androl 25:625–629
Wolk R, Smith WB, Neutel JM et al (2009) Blood pressure lowering effects of a new long-acting inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 5 in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Hypertension 53:1091–1097
Webb DJ, Freestone S, Allen MJ et al (1999) Sildenafil citrate and blood-pressure-lowering drugs: results of drug interaction studies with an organic nitrate and a calcium antagonist. Am J Cardiol 83:21C–28C
Zusman RM, Prisant LM, Brown MJ (2000) Effect of sildenafil citrate on blood pressure and heart rate in men with erectile dysfunction taking concomitant antihypertensive medication. Sildenafil Study Group. J Hypertens 18:1865–1869
Pickering TG, Shepherd AM, Puddey I et al (2004) Sildenafil citrate for erectile dysfunction in men receiving multiple antihypertensive agents: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Hypertens 17:1135–1142
Ghiadoni L, Versari D, Taddei S (2008) Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition in essential hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 10:52–57
Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Ferrebuz A, Vanegas V et al (2005) Early treatment with cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor ameliorates progression of renal damage. Kidney Int 68:2131–2142
Gardiner SM, March JE, Kemp PA et al (2005) Hemodynamic effects of phosphodiesterase 5 and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition alone or in combination in conscious SHR. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:265–271
Komers R, Anderson S (2003) Paradoxes of nitric oxide in the diabetic kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F1121–F1137
Craven PA, Studer RK, DeRubertis FR (1994) Impaired nitric oxide-dependent cyclic guanosine monophosphate generation in glomeruli from diabetic rats. Evidence for protein kinase C-mediated suppression of the cholinergic response. J Clin Invest 93:311–320
Jeong KH, Lee TW, Ihm CG et al (2009) Effects of sildenafil on oxidative and inflammatory injuries of the kidney in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Am J Nephrol 29:274–282
Fang L, Radovits T, Szabo G et al (2013) Selective phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitor vardenafil ameliorates renal damage in type 1 diabetic rats by restoring cyclic 3′,5′ guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) level in podocytes. Nephrol Dial Transpl 28:1751–1761
Scheele WH, Gale JD, Clein V, Tamimi N, Le V, Walley RJ, Paez FG, El-Nahas M (2014) Selective inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 5 reduces macroalbuminuria in subjects with type 2 diabetes, and overt nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol Abstr (Suppl. 25)
Santi D, Giannetta E, Isidori AM et al (2015) THERAPY OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: effects of chronic use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on endothelial markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol 172:R103–R114
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M et al (2012) Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 298:229–317
Cadirci E, Halici Z, Odabasoglu F et al (2011) Sildenafil treatment attenuates lung and kidney injury due to overproduction of oxidant activity in a rat model of sepsis: a biochemical and histopathological study. Clin Exp Immunol 166:374–384
Choi DE, Jeong JY, Lim BJ et al (2009) Pretreatment of sildenafil attenuates ischemia-reperfusion renal injury in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F362–F370
Kucuk A, Yucel M, Erkasap N et al (2012) The effects of PDE5 inhibitory drugs on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Biol Rep 39:9775–9782
Guzeloglu M, Yalcinkaya F, Atmaca S et al (2011) The beneficial effects of tadalafil on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Urol Int 86:197–203
Faddegon S, Best SL, Olweny EO et al (2012) Tadalafil for prevention of renal dysfunction secondary to renal ischemia. Can J Urol 19:6274–6279
Hosgood SA, Randle LV, Patel M et al (2014) Sildenafil citrate in a donation after circulatory death experimental model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplantation 98:612–617
Guan Z, Miller SB, Greenwald JE (1995) Zaprinast accelerates recovery from established acute renal failure in the rat. Kidney Int 47:1569–1575
Solomon RJ, Mehran R, Natarajan MK et al (2009) Contrast-induced nephropathy and long-term adverse events: cause and effect? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1162–1169
Lauver DA, Carey EG, Bergin IL et al (2014) Sildenafil citrate for prophylaxis of nephropathy in an animal model of contrast-induced acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 9:e113598
Selby NM, Shaw S, Woodier N et al (2009) Gentamicin-associated acute kidney injury. QJM 102:873–880
Morsy MA, Ibrahim SA, Amin EF et al (2014) Sildenafil ameliorates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: role of iNOS and eNOS. J Toxicol 2014:489382
Abdel-latif RG, Morsy MA, El-Moselhy MA et al (2013) Sildenafil protects against nitric oxide deficiency-related nephrotoxicity in cyclosporine A treated rats. Eur J Pharmacol 705:126–134
Essiz D, Sozmen M, Sudagidan M, et al (2015) Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition attenuates cyclosporine A induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Biotech Histochem 90(3):167–178
Hosogai N, Tomita M, Hamada K et al (2003) Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition ameliorates nephrotoxicity induced by cyclosporin A in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 477:171–178
Whitaker RM, Wills LP, Stallons LJ et al (2013) cGMP-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and promote recovery from acute kidney injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 347:626–634
Lledo-Garcia E, Subira-Rios D, Ogaya-Pinies G et al (2011) Intravenous sildenafil as a preconditioning drug against hemodynamic consequences of warm ischemia-reperfusion on the kidney. J Urol 186:331–333
Serhatlioglu S, Kiris A, Kocakoc E et al (2003) Evaluation of the effects of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on canine renal artery, carotid and aortic blood flow with the aid of color Doppler sonography. Urol Int 71:103–107
Ardicoglu A, Kocakoc E, Yuzgec V et al (2005) Hemodynamic effects of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on segmental branches of bilateral renal arteries. Int Urol Nephrol 37:785–789
Degirmenci B, Acar M, Albayrak R et al (2006) Effects of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on renal arteries: an evaluation with Doppler ultrasound. Urol Int 77:170–172
Dias AT, Rodrigues BP, Porto ML et al (2014) Sildenafil ameliorates oxidative stress and DNA damage in the stenotic kidneys in mice with renovascular hypertension. J Transl Med 12:35
Tapia E, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Soto V et al (2012) Sildenafil treatment prevents glomerular hypertension and hyperfiltration in rats with renal ablation. Kidney Blood Press Res 35:273–280
Lau DH, Mikhailidis DP, Thompson CS (2007) The effect of vardenafil (a PDE type 5 inhibitor) on renal function in the diabetic rabbit: a pilot study. In Vivo 21:851–854
Rosano GM, Aversa A, Vitale C et al (2005) Chronic treatment with tadalafil improves endothelial function in men with increased cardiovascular risk. Eur Urol 47:214–220; discussion 220–222
Yildiz H, Durmus AS, Simsek H et al (2011) Effects of sildenafil citrate on torsion/detorsion-induced changes in red blood cell and plasma lipid peroxidation, antioxidants, and blood hematology of male rats. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 159:359–363
Hohenstein B, Daniel C, Wittmann S et al (2008) PDE-5 inhibition impedes TSP-1 expression, TGF-beta activation and matrix accumulation in experimental glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transpl 23:3427–3436
Acknowledgments
AO was supported by PI13/00047, PIE13/00051, ISCIII-RETIC REDinREN RD12/0021 Fondos FEDER, S2010/BMD-2378, FRIAT-IRSIN, and Programa Intensificación Actividad Investigadora (ISCIII/Agencia Laín-Entralgo/CM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest between the authors.
Ethical approval
This is a review and no need for ethical approval. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afsar, B., Ortiz, A., Covic, A. et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors and kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 1521–1528 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1071-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1071-4