Abstract
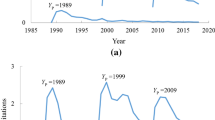
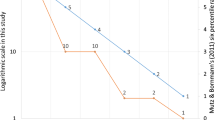
In this article I study characteristics of the journal impact factor (JIF) computed using a 5-year citation window as compared with the classical JIF computed using a 2-year citation window. Since 2007 ISI-Thomson Reuters has published the new 5-year impact factor in the JCR database. I studied changes in the distribution of JIFs when the citation window was enlarged. The distributions of journals according their 5-year JIFs were very similar all years studied, and were also similar to the distribution according to the 2-year JIFs. In about 72% of journals, the JIF increased when the longer citation window was used. Plots of 5-year JIFs against rank closely followed a beta function with two exponents. Thus, the 5-year JIF seems to behave very similarly to the 2-year JIF. The results also suggest that gains in JIF with the longer citation window tend to distribute similarly in all years. Changes in these gains also tend to distribute similarly from 1 year to the following year.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, M., & Mabe, M. (2000). Impact factors: Use and abuse. Perspectives in Publishing, 1, 1–6.
Archambault, E., & Larivière, V. (2009). History of the journal impact factor: Contingencies and consequences. Scientometrics, 79, 635–649.
Bar-Ilan, J. (2008). Informetrics at the beginning of the 21st century—A review. Journal of Informetrics, 2, 1–52.
Bensman, S. J. (2007). Garfield and the impact factor. Annual Review of Information Science and Technology, 41, 93–155.
Brown, A. (2007). How impact factors changed medical publishing-and science. British Medical Journal, 334, 561–564.
Campanario, J. M. (2010). Distribution of changes in impact factors over time. Scientometrics, 84, 35–42.
Franceschet, M. (2010). Journal influence factors. Journal of Informetrics, 4, 239–248.
Garfield, E. (1955). Citation indexes to science: A new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Science, 122, 108–111.
Glänzel, W., & Moed, H. F. (2002). Journal impact measures in bibliometric research. Scientometrics, 53, 171–193.
Gomez-Sancho, J. M., & Mancebon-Torrubia, M. J. (2009). The evaluation of scientific production: Towards a neutral impact factor. Scientometrics, 81, 435–458.
Jacso, P. (2009). Five-year impact factor data in the Journal Citation Reports. Online Information Review, 33, 603–614.
Kleijnen, J. P. C., & Van Groenendaal, W. (2000). Measuring the quality of publications: New methodology and case study. Information Processing & Management, 36, 551–570.
Kuo, W., & Rupe, J. (2007). R-impact factor: Reliability-based citation impact factor. IEEE Transaction on Reliability, 56, 366–367.
Mansilla, R., Köppen, E., Cocho, G., & Miramontes, P. (2007). On the behavior of journal impact factor rank-order distribution. Journal of Informetrics, 1, 155–160.
Neuhaus, C., Marx, W., & Daniel, H. D. (2009). The publication and citation impact profiles of Angewandte Chemie and the Journal of the American Chemical Society based on the sections of Chemical Abstracts: A case study on the limitations of the journal impact factor. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60, 176–183.
Rossner, M., Van Epps, H., & Hill, E. (2007). Show me the data. Journal of Cell Biology, 179, 1091–1092.
Rossner, M., Van Epps, H., & Hill, E. (2008). Irreproducible results: A response to Thomson Scientific. Journal of Cell Biology, 180, 254–255.
Rousseau, R. (1988). Citation distribution of pure mathematics journals. In L. Egghe & R. Rousseau (Eds.), Informetrics 87/88 (pp. 249–262). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Rousseau, R., Jin, B., & Yang, N. (2001). Observations concerning the two- and three-year synchronous impact factor, based on the Chinese science citation database. Journal of Documentation, 57, 349–357.
Rowlands, I. (2002). Journal diffusion factors: A new approach to measuring research influence. Aslib Proceedings, 54, 77–84.
Sombatsompop, N., Markpin, T., & Premkamolnetr, N. (2004). A modified method for calculating the Impact Factors of journals in ISI Journal Citation Reports: Polymer Science category in 1997–2001. Scientometrics, 60, 217–235.
Stimulate 9 Group A. (2009). The 5-year synchronous impact factor for large JCR subject areas. Cybermetrics, 13, http://www.cindoc.csic.es/cybermetrics/articles/v13i1p5.html. Accessed 11 November 2010.
Van Leeuwen, T. N., & Moed, H. F. (2002). Development and application of journal impact measures in the Dutch science system. Scientometrics, 53, 249–266.
Van Leeuwen, T. N., Moed, H. F., & Reedijk, J. (1999). Critical comments on Institute for Scientific Information impact factors: A sample of inorganic molecular chemistry journals. Journal of Information Science, 25, 489–498.
Vanclay, J. K. (2009). Bias in the journal impact factor. Scientometrics, 78, 3–12.
Walter, G., Bloch, S., Hunt, G., & Fisher, K. (2003). Counting on citations: A flawed way to measure quality. Medical Journal of Australia, 178, 280–283.
Yu, G., Yang, D. H., & Liang, W. (2010). Reliability-based citation impact factor and the manipulation of impact factor. Scientometrics, 83, 259–270.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology (Dirección General de Investigación) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF/FEDER, project SEJ2007-66236/SOCI). I thank K. Shashok for improving the use of English in the manuscript and for suggestions about the content and two anonymous referees for their suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campanario, J.M. Empirical study of journal impact factors obtained using the classical two-year citation window versus a five-year citation window. Scientometrics 87, 189–204 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0334-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0334-1