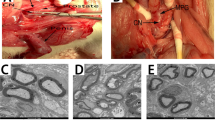
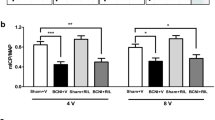
Abstract
It was recently reported in the rat that vardenafil given in a continuous long-term manner was successful in preventing smooth muscle fibrosis in the penile corpora cavernosa and corporal veno-occlusive dysfunction (CVOD) that occur following bilateral cavernosal nerve resection (BCNR), a model for human erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy. To expand on this finding and to determine whether this effect was common to other PDE5 inhibitors, and occurred in part by stimulation of the spontaneous induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, also known as NOS2), male Fischer 344 rats (N=10/group) were subjected to either BCNR or unilateral cavernosal nerve resection (UCNR) and treated with sildenafil (20 mg kg−1 day−1) in the drinking water daily for 45 days. Additional BCNR groups received L-NIL (6.7 mg kg−1 day−1) as inhibitor of iNOS activity, with or without concurrent sildenafil administration. It was determined that sildenafil, like vardenafil, (1) prevented the 30% decrease in the smooth muscle cell/collagen ratio, and the 3–4-fold increase in apoptosis and reduction in cell proliferation, and partially counteracted the increase in collagen, seen with both UCNR and BCNR; and (2) normalized the CVOD, measured by dynamic infusion cavernosometry, induced by both BCNR and UCNR. The long-term inhibition of iNOS activity exacerbated corporal fibrosis and CVOD in the BCNR rats, but sildenafil functional effects were not affected by L-NIL. These data suggest that the salutary effects of continuous long-term PDE5 inhibitors on erectile function post-cavernosal nerve resection involve their ability to prevent the alterations in corporal histology induced by cavernosal nerve damage, in a process apparently independent from endogenous iNOS induction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Montorsi F, Burnett AL . Erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 2004; 93: 1–2.
Menon M, Kaul S, Bhandari A, Shrivastava A, Tewari A, Hemal A . Potency following robotic radical prostatectomy a questionnaire based analysis of outcomes after conventional nerve sparing and prostatic fascia sparing techniques. J Urol 2005; 174: 2291–2296.
Montorsi F, McCullough A . Efficacy of sildenafil citrate in men with erectile dysfunction following radical prostatectomy: a systematic review of clinical data. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 658–667.
Mulhall JP, Slovick R, Hotaling J, Aviv N, Valenzuela R, Waters WB et al. Erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy hemodynamic profiles and their correlation with the recovery of erectile function. J Urol 2002; 167: 1371–1375.
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Ignarro LJ, Rajfer J . Nitric oxide and the cyclic GMP system in the penis. Mol Urol 1999; 3: 51–59.
Iacono F, Giannella R, Somma P, Manno G, Fusco F, Mirone V . Histological alterations in cavernous tissue after radical prostatectomy. J Urol 2005; 173: 1673–1676.
Schwartz EJ, Wong P, Graydon RJ . Sildenafil preserves intracorporeal smooth muscle after radical retropubic prostatectomy. J Urol 2004; 171: 771–774.
Yaman O, Yilmaz E, Bozlu M, Anafarta K . Alterations of intracorporeal structures in patients with erectile dysfunction. Urol Int 2003; 71: 87–90.
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J . Molecular pathophysiology and gene therapy of aging-related erectile dysfunction. Exptl Gerontol 2004; 39: 1705–1712.
Montorsi F, Briganti A, Salonia A, Rigatti P, Burnett AL . Current and future strategies for preventing and managing erectile dysfunction following radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 2004; 45: 123–133.
Davila HH, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF . Corporal veno-occlusive dysfunction in the aging rat evaluation by cavernosometry and cavernosography. Urology 2004; 64: 1261–1266.
Ferrini MG, Kovanecz I, Sanchez S, Vernet D, Davila HH, Rajfer J et al. Long-term continuous treatment with sildenafil in the rat ameliorates aging-related erectile dysfunction and the underlying corporal fibrosis. Biol Reprod 2007; 76: 915–923. epub ahead of print.
Kovanecz I, Ferrini MG, Vernet D, Nolazco G, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF . Pioglitazone prevents corporal veno-occlusive dysfunction (CVOD) in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. BJU Int 2006; 98: 116–124.
Khatib AM, Siegfried G, Messai H, Moldovan F, Mitrovic DR . Mechanism of inhibition of endothelin-1-stimulated proteoglycan and collagen synthesis in rat articular chondrocytes. Cytokine 2002; 17: 254–261.
Wang S, Wu X, Lincoln TM, Murphy-Ullrich JE . Expression of constitutively active cGMP-dependent protein kinase prevents glucose stimulation of thrombospondin 1 expression and TGF-beta activity. Diabetes 2003; 52: 2144–2150.
Saura M, Zaragoza C, Herranz B, Griera M, Diez-Marques L, Rodriguez-Puyol D et al. Nitric oxide regulates transforming growth factor-beta signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 2005; 97: 1115–1123.
Li P, Oparil S, Novak L, Cao X, Shi W, Lucas JA et al. ANP signaling inhibits TGF {beta}-induced Smad2 and Smad3 nuclear translocation and extracellular matrix expression in rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Appl Physiol 2006; 102: 390–398 epub ahead of print.
Nagel DJ, Aizawa T, Jeon KI, Liu W, Mohan A, Wei H et al. Role of nuclear Ca2+/calmodulin-stimulated phosphodiesterase 1A in vascular smooth muscle cell growth and survival. Circ Res 2006; 98: 777–784.
Pan SL, Guh JH, Chang YL, Kuo SC, Lee FY, Teng CM . YC-1 prevents sodium nitroprusside-mediated apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 2004; 61: 152–158.
Das A, Xi L, Kukreja RC . Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil preconditions adult cardiac myocytes against necrosis and apoptosis. Essential role of nitric oxide signaling. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 12944–12955.
Gobeil Jr F, Zhu T, Brault S, Geha A, Vazquez-Tello A, Fortier A et al. Nitric oxide signaling via nuclearized endothelial nitric-oxide synthase modulates expression of the immediate early genes iNOS and mPGES-1. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 16058–16067.
Hayden MA, Nakayama DK . Cyclic nucleotides and inducible nitric oxide synthesis in pulmonary artery smooth muscle. J Surg Res 1999; 82: 222–227.
Perez-Sala D, Cernuda-Morollon E, Diaz-Cazorla M, Rodriguez-Pascual F, Lamas S . Posttranscriptional regulation of human iNOS by the NO/cGMP pathway. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2001; 280: F466–F473.
Hochberg D, Johnson CW, Chen J, Cohen D, Stern J, Vaughan Jr ED et al. Interstitial fibrosis of unilateral ureteral obstruction is exacerbated in kidneys of mice lacking the gene for inducible nitric oxide synthase. Lab Invest 2000; 80: 1721–1728.
Chen Y, Hozawa S, Sawamura S, Sato S, Fukuyama N, Tsuji C et al. Deficiency of inducible nitric oxide synthase exacerbates hepatic fibrosis in mice fed high-fat diet. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 326: 45–51.
Ferrini MG, Vernet D, Magee TR, Shahed A, Quian A, Rajfer J et al. Antifibrotic role of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Nitric Oxide 2002; 6: 1–12.
Davila HH, Magee TR, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF . Gene therapy with the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) cDNA regresses the fibrotic plaque in an animal model of Peyronie's disease. Biol Reprod 2004; 71: 1568–1577.
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J . The pleiotropic effects of inducible nitric oxide synthase on the physiology and pathology of penile erection. Curr Pharm Des 2005; 11: 4041–4046.
Ferrini MG, Davila H, Valente EG, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J . Aging-related induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2A) is vasculo-protective in the arterial media. Cardiovasc Res 2004; 61: 796–805.
Zhang JJ, Bledsoe G, Kato K, Chao L, Chao J . Tissue kallikrein attenuates salt-induced renal fibrosis by inhibition of oxidative stress. Kidney Int 2004; 66: 722–732.
Hewitson TD, Martic M, Darby IA, Kelynack KJ, Bisucci T, Tait MG et al. Intracellular cyclic nucleotide analogues inhibit in vitro mitogenesis and activation of fibroblasts derived from obstructed rat kidneys. Nephron Exp Nephrol 2004; 96: e59–e66.
Vernet D, Ferrini MG, Valente E, Magee TR, Bou-Gharios G, Rajfer J et al. Effect of nitric oxide on fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts in cell cultures from the Peyronie's fibrotic plaque and in its rat model in vivo. Nitric Oxide 2002; 7: 262–276.
Klein LT, Miller MI, Buttyan R, Raffo AJ, Burchard M, Devris G et al. Apoptosis in the rat penis after penile denervation. J Urol 1997; 158: 626–630.
User HM, Hairston JH, Zelner DJ, McKenna KE, McVary KT . Penile weight and cell subtype specific changes in a post-radical prostatectomy model of erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2003; 169: 1175–1179.
Leungwattanakij S, Bivalacqua TJ, Usta MF, Yang DY, Hyun JS, Champion HC et al. Cavernous neurotomy causes hypoxia and fibrosis in rat corpus cavernosum. J Androl 2003; 24: 239–249.
Ferrini MG, Davila HH, Kovanecz I, Sanchez SP, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J . Vardenafil prevents fibrosis and loss of corporal smooth muscle that occurs after bilateral cavernosal nerve resection in the rat. Urology 2006; 68: 429–435.
Ferrini MG, Kovanecz I, Nolazco G, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF . Effects of long-term treatment with vardenafil on the development of the fibrotic plaque in a rat model of Peyronie's disease. BJU Int 2006; 97: 625–633.
Valente EG, Vernet D, Ferrini MG, Qian A, Rajfer J, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF . PDE L-arginine and PDE inhibitors counteract fibrosis in the Peyronie's fibrotic plaque and related fibroblast cultures. Nitric Oxide 2003; 9: 229–244.
Shin HS, Bae SK, Lee MG . Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after intravenous and oral administration in rats: hepatic and intestinal first-pass effects. Int J Pharm 2006; 320: 64–70.
Orlandi A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G, Spagnoli LG . Aging, smooth muscle cells and vascular pathobiology: implications for atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2006; 188: 221–230.
Musicki B, Champion HC, Becker RE, Kramer MF, Liu T, Sezen SF et al. In vivo analysis of chronic phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition with sildenafil in penile erectile tissues: no tachyphylaxis effect. J Urol 2005; 174: 1493–1496.
Behr-Roussel D, Gorny D, Mevel K, Caisey S, Bernabe J, Burgess G et al. Chronic sildenafil improves erectile function and endothelium dependent cavernosal relaxations in rats: lack of tachyphylaxis. Eur Urol 2005; 47: 87–91.
Musicki B, Champion HC, Becker RE, Liu T, Kramer MF, Burnett AL . Erection capability is potentiated by long-term sildenafil treatment: role of blood flow-induced endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol 2005; 68: 226–232.
Ghofrani HA, Osterloh IH, Grimminger F . Sildenafil: from angina to erectile dysfunction to pulmonary hypertension and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 689–702.
Lu SY, Wang DS, Zhu MZ, Zhang QH, Hu YZ, Pei JM . Inhibition of hypoxia-induced proliferation and collagen synthesis by vasonatrin peptide in cultured rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 2005; 77: 28–38.
Rosanio S, Ye Y, Atar S, Rahman AM, Freeberg SY, Huang MH et al. Enhanced cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury with combining sildenafil with low-dose atorvastatin. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2006; 20: 27–36.
Salloum F, Yin C, Xi L, Kukreja RC . Sildenafil induces delayed preconditioning through inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent pathway in mouse heart. Circ Res 2003; 92: 595–597.
Wharton J, Strange JW, Moller GM, Growcott EJ, Ren X, Franklyn AP et al. Antiproliferative effects of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition in human pulmonary artery cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 172: 105–113.
Pilz RB, Casteel DE . Regulation of gene expression by cyclic GMP. Circ Res 2003; 93: 1034–1046.
Ferrini MG, Nolazco G, Vernet D, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Berman J . Increased vaginal oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inducible nitric oxide synthase in a diabetic rat model: implications for vaginal fibrosis. Fertil Steril 2006; 86: 1152–1163.
Smith Jr RS, Agata J, Xia CF, Chao L, Chao J . Human endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene delivery protects against cardiac remodeling and reduces oxidative stress after myocardial infarction. Life Sci 2005; 76: 2457–2471.
Craven PA, Studer RK, Felder J, Phillips S, DeRubertis FR . Nitric oxide inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta and collagen synthesis in mesangial cells. Diabetes 1997; 46: 671–681.
Lincoln TM, Wu X, Sellak H, Dey N, Choi CS . Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype by cyclic GMP and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. Front Biosci 2006; 11: 356–367.
Desouza C, Parulkar A, Lumpkin D, Akers D, Fonseca VA . Acute and prolonged effects of sildenafil on brachial artery flow-mediated dilatation in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 1336–1339.
Rosano GM, Aversa A, Vitale C, Fabbri A, Fini M, Spera G . Chronic treatment with tadalafil improves endothelial function in men with increased cardiovascular risk. Eur Urol 2005; 47: 214–220; discussion 220–222.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a grant from Pfizer Corp., and in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01DK-53069 and G12RR-03026), and the Department of Defense (PC061300). Dr Monica Ferrini was partially funded by NIH grant 5P20MD000545
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovanecz, I., Rambhatla, A., Ferrini, M. et al. Long-term continuous sildenafil treatment ameliorates corporal veno-occlusive dysfunction (CVOD) induced by cavernosal nerve resection in rats. Int J Impot Res 20, 202–212 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901612
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901612
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence of post-prostatectomy erectile dysfunction and a review of the recommended therapeutic modalities
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)
-
Sildenafil in postprostatectomy erectile dysfunction (perspective)
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)
-
The two phases of the clinical validation of preclinical translational mechanistic research on PDE5 inhibitors since Viagra’s advent. A personal perspective
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)
-
Non-invasive Management Options for Erectile Dysfunction When a Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor Fails
Drugs & Aging (2018)
-
The application of wrapping ureter by a pedicled gastrocolic omentum flap combined with an artificial external scaffold to prevent stoma stenosis in rabbit after ureterocutaneostomy
International Urology and Nephrology (2017)