Abstract
Background
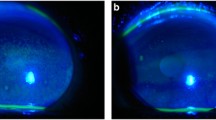
Vortex keratopathy, arising as a side effect of several medications, is characterized by golden-brown deposits in the cornea.
Methods
A 41-year-old woman treated for sarcoidosis with hydroxychloroquine therapy and suffering from vortex keratopathy was examined by in vivo confocal microscopy. Scans of both corneas were performed.
Results
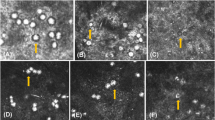
By slit lamp examination, the left but not the right eye showed a golden-brown deposit throughout the cornea. In vivo confocal microscopy revealed the presence of highly reflective, dot-like intracellular inclusions concentrated in the basal epithelial layer. They were also detected within the anterior and posterior stroma, but not within the endothelium. In regions of the anterior stroma, devoid of inclusions, hyperreflective ramified keratocytes were observed, forming an extended interconnecting network.
Conclusion
In addition to the granular deposits, in vivo confocal microscopy revealed hyperreflective, possibly phagocytic keratocytes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakravarti S, Wu F, Vij N, Roberts L, Joyce S (2004) Microarray studies reveal macrophage-like function of stromal keratocytes in the cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:3475–3484
Ciancaglini M, Carpineto P, Zuppardi E, Nubile M, Doronzo E, Mastropasqua L (2001) In vivo confocal microscopy of patients with amiodarone-induced keratopathy. Cornea 20:368–373
D’Amico DJ, Kenyon KR, Ruskin JN (1981) Amiodarone keratopathy: drug-induced lipid storage disease. Arch Ophthalmol 99:257–261
Dua HS, Singh A, Gomes JA, Laibson PR, Donoso LA, Tyagi S (1996) Vortex or whorl formation of cultured human corneal epithelial cells induced by magnetic fields. Eye 10(Pt 4):447–450
Hirst LW, Sanborn G, Green WR, Miller NR, Heath WD (1982) Amodiaquine ocular changes. Arch Ophthalmol 100:1300–1304
Hollander DA, Aldave AJ (2004) Drug-induced corneal complications. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 15:541–548
Ingram DV, Jaggarao NS, Chamberlain DA (1982) Ocular changes resulting from therapy with amiodarone. Br J Ophthalmol 66:676–679
Poole CA, Brookes NH, Clover GM (2003) Confocal imaging of the human keratocyte network using the vital dye 5-chloromethylfluorescein diacetate. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 31:147–154
Pulhorn G, Thiel HJ (1976) [Ultrastructural aspects of chloroquin-keratopathy (author’s transl)]. Albrecht Von Graefe's Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol 201:89–99
Slowik C, Somodi S, von Gruben C, Richter A, Guthoff R (1997) [Detection of morphological corneal changes caused by chloroquine therapy using confocal in vivo microscopy]. Ophthalmologe 94:147–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dosso, A., Rungger-Brändle, E. In vivo confocal microscopy in hydroxychloroquine-induced keratopathy. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245, 318–320 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-006-0365-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-006-0365-8