Abstract
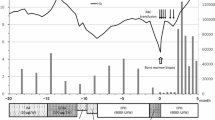
We describe a middle-aged Chinese systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patient developing steroid refractory and transfusion dependent red cell aplasia. Oral danazol 200 mg twice per day was started together with low-dose prednisolone therapy. There was no further recurrence of anemia 1 month after this combined therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi BG, Yoo WH (2002) Successful treatment of pure red cell aplasia with plasmapheresis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Yonsei Med J 43(2):274–278
Kiely PD, McGuckin CP, Collins DA, Bevan DH et al (1995) Erythrocyte aplasia and systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 4:407–411
Linardaki GD, Boki KA, Fartakis A, Tzioufas AG (1999) Pure red cell aplasia as presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus: Antibodies to erythropoietin. Scand J Rheumatol 28:189–191
Abkowitz JL, Kadin ME, Powell JS, Adamson JW (1986) Pure red cell aplasia: lymphocyte inhibition of erythropoiesis. Br J Haematol 63:59–67
Clark DA, Dessypris EN, Krantz SB (1984) Studies on pure red cell aplasia. XI. Results of immunosuppressive treatment of 37 patients. Blood 63:277
Winkler A, Jackson RW, Kay DS (1988) High dose intravenous cyclophosphamide treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus associated aplastic anemia. Arthritis Rheum 31:693
Duarte-Salazar C, Cazarin-Barrientos J, Goycochea-Robles MV, Collazo-Jaloma J et al (2000) Successful treatment of pure red cell aplasia associated with systemic lupus erythematosus with cyclosporin A. Rheumatol 39:1155–1157
Ilan Y, Naparstek Y (1993) Pure red cell aplasia associated with systemic lupus erythematosus: remission after a single course of intravenous immunoglobulin. Acta Haematol 89:152–154
Lippman SM, Durie BGM, Garewal HS, Giordano G et al (1986) Efficacy of danazol in pure red cell aplasia. Am J Hematol 23:373–379
Roubinian JR, Papoian R, Talal N (1977) Androgenic hormones modulate autoantibody responses and improve survival in murine lupus. J Clin Invest 59:1066–1070
Roubinian JR, Talal N, Greenspan JS, Goodman JR et al (1978) Effect of castration and sex hormone treatment on survival, anti-nucleic acid antibodies, and glomerulonephritis in NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Exp Med 147:1568–1583
Michalski JP, McCombs CC, Roubinian JR, Talal N (1983) Effect of androgen therapy on survival and suppressor cell activity in aged NZB/NZW F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol 52:229–233
Stein CM (2001) Immunoregulatory drugs. In: Ruddy S (ed) Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 879–898
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, A.Y., Li, E.K., Tam, L. et al. Successful treatment of pure red cell aplasia associated with systemic lupus erythematosus with oral danazol and steroid. Rheumatol Int 25, 388–390 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-004-0521-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-004-0521-6